
ICIP 2021 - The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Compressive Covariance Matrix Estimation from a Dual-Dispersive Coded Aperture Spectral Imager
- Log in to post comments
Compressive covariance sampling (CCS) theory aims to recover the covariance matrix (CM) of a signal, instead of the signal itself, from a reduced set of random linear projections. Although several theoretical works demonstrate the CCS theory's advantages in compressive spectral imaging tasks, a real optical implementation has not been proposed.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about A FOVEATED VIDEO QUALITY ASSESSMENT MODEL USING SPACE-VARIANT NATURAL SCENE STATISTICS
- Log in to post comments
In Virtual Reality (VR) systems, head mounted displays (HMDs) are widely used to present VR contents. When displaying immersive (360 degree video) scenes, greater challenges arise due to limitations of computing power, frame rate, and transmission bandwidth. To address these problems, a variety of foveated video compression and streaming methods have been proposed, which seek to exploit the nonuniform sampling density of the retinal photoreceptors and ganglion cells, which decreases rapidly with increasing eccentricity.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about CFPNET: CHANNEL-WISE FEATURE PYRAMID FOR REAL-TIME SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Real-time semantic segmentation is playing a more important role in computer vision, due to the growing demand for mobile devices and autonomous driving. Therefore, it is very important to achieve a good trade-off among performance, model size and inference speed. In this paper, we propose a Channel-wise Feature Pyramid (CFP) module to balance those factors. Based on the CFP module, we built CFPNet for real-time semantic segmentation which applied a series of dilated convolution channels to extract effective features.
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 Views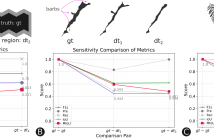
- Read more about Multiscale IoU: A Metric for Evaluation of Salient Object Detection with Fine Structures
- Log in to post comments
General-purpose object-detection algorithms often dismiss the fine structure of detected objects. This can be traced back to how their proposed regions are evaluated. Our goal is to renegotiate the trade-off between the generality of these algorithms and their coarse detections. In this work, we present a new metric that is a marriage of a popular evaluation metric, namely Intersection over Union (IoU), and a geometrical concept, called fractal dimension. We propose Multiscale IoU (MIoU) which allows comparison between the detected and ground-truth regions at multiple resolution levels.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views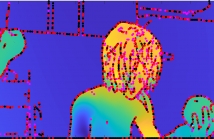
- Read more about Scalable Coding of Motion and Depth Fields with Shared Breakpoints
- Log in to post comments
A new breakpoint adaptive DWT, referred to as tri-break, is currently
being considered by standardization efforts in relation to JPEG 2000
Part 17 extensions. We first provide a summary of the tri-break transform
and then explore its performance for coding motion fields. Experimental
results show that significant gains can be achieved for
coding piecewise smooth motion flows by employing the tri-break
transform. We demonstrate the feasibility of utilising a common set
of breakpoints for compressing depth maps and motion fields anchored
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Listen to the Pixels
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Performing sound source separation and visual object segmentation jointly in naturally occurring videos is a notoriously difficult task, especially in the absence of annotated data. In this study, we leverage the concurrency between audio and visual modalities in an attempt to solve the joint audio-visual segmentation problem in a self-supervised manner. Human beings interact with the physical world through a few sensory systems such as vision, auditory, movement, etc. The usefulness of the interplay of such systems lies in the concept of degeneracy.
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views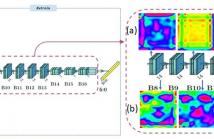
- Read more about MICRO-EXPRESSION RECOGNITION BASED ON VIDEO MOTION MAGNIFICATION AND PRE-TRAINED NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates the effects of using video motion magnification methods based on amplitude and phase, respectively, to amplify small facial movements. We hypothesise that this approach will assist in the micro-expression recognition task. To this end, we apply the pre-trained VGGFace2 model with its excellent facial feature capturing ability to transfer learn the magnified micro-expression movement, then encode the spatial information and decode the spatial and temporal information by Bi-LSTM model.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Adversarial Unsupervised Video Summarization Augmented with Dictionary Loss
- Log in to post comments
Automated unsupervised video summarization by key-frame extraction consists in identifying representative video frames, best abridging a complete input sequence, and temporally ordering them to form a video summary, without relying on manually constructed ground-truth key-frame sets. State-of-the-art unsupervised deep neural approaches consider the desired summary to be a subset of the original sequence, composed of video frames that are sufficient to visually reconstruct the entire input.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views