
ICIP 2021 - The International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), sponsored by the IEEE Signal Processing Society, is the premier forum for the presentation of technological advances and research results in the fields of theoretical, experimental, and applied image and video processing. ICIP has been held annually since 1994, brings together leading engineers and scientists in image and video processing from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Inverse Halftone Colorization: Making Halftone Prints Color Photos
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
A learning algorithm referred to as Maximum Margin (MM) is proposed for considering the class-imbalance data learning issue: the deep model tends to predict the majority classes rather than the minority ones. For better generalization on the minority classes, the proposed Maximum Margin (MM) loss function is newly designed by minimizing a margin-based generalization bound through the shifting decision bound. As a prior study, the theoretically principled label-distributionaware margin (LDAM) loss had been successfully applied with classical strategies such as re-weighting or re-sampling.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Motivating bilevel approaches to filter learning: A case study
- Log in to post comments
The recent trend in regularization methods for inverse problems is to replace handcrafted sparsifying operators with data-driven approaches. Although using such machine learning techniques often improves image reconstruction methods, the results can depend significantly on the learning methodology. This paper compares two supervised learning methods. First, the paper considers a transform learning approach and, to learn the transform, introduces a variant on the Procrustes method for wide matrices with orthogonal rows. Second, we consider a bilevel convolutional filter learning approach.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Piecewise Bézier space: Recovering 3D dynamic motion from video
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we address the problem of jointly retrieving a 3D dynamic shape, camera motion, and deformation grouping from partial 2D point trajectories in a monocular video. To this end, we introduce a union of piecewise Bézier subspaces with enforcing continuities to model 3D motion. We show that formulating the problem in terms of piecewise curves, allows for a better physical interpretation of the resulting priors and a more accurate representation of the motion.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views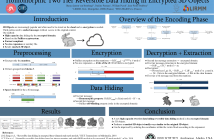
- Read more about Homomorphic Two Tier Reversible Data Hiding in Encrypted 3D Objects
- Log in to post comments
Today, 3D objects are an increasingly popular form of media. It has become necessary to secure them during their transmission or archiving. In this paper, we propose a two tier reversible data hiding method for 3D objects in the encrypted domain. Based on the homomorphic properties of the Paillier cryptosystem, our proposed method embeds a first tier message in the encrypted domain which can be extracted in either the encrypted domain or the clear domain. Indeed, our method produces a marked 3D object which is visually very similar to the original object.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about ITERATIVE SUBNETWORK WITH LINEAR HIERARCHICAL ORDERING FOR HUMAN POSE ESTIMATION
- Log in to post comments
Human pose estimation is a long-standing and challenging problem in computer vision. Many recent advancements in the field have relied on complex structure refinement and specific human joint graphical relations. However, progress has been saturated in terms of accuracy. Each time, new state-of-the-art approaches only improve accuracy by less than 0.3% in the MPII test set despite using complicated model structures.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
At present, the performance of the end-to-end stereo matching networks based on CNN greatly exceed the traditional stereo matching networks, but the accuracy in those ill-posed regions like foreground areas is still not optimistic. In this paper, we propose a novel design to improve the prediction performance of disparity in foreground. First, a multi-scale pyramid aggregation module with hourglass-like structure is designed to effectively utilize the aggregation information of different scales.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Signal Variances: CNN Initialization Through Modern Architectures
- Log in to post comments
Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), renowned for their consistent performance, are widely understood by practitioners that the stability of learning depends on the initialization of the model parameters in each layer. Kaiming initialization, the de facto standard, is derived from a much simpler CNN model which consists of only the convolution and fully connected layers. Compared to the current CNN models, the basis CNN model for the Kaiming initialization does not include the max pooling or global average pooling layers.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Evolving deep ensembles for detecting COVID-19 in chest X-Rays
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Class Specific Interpretability in CNN Using Causal Analysis
- Log in to post comments
A singular problem that mars the wide applicability of machine learning (ML) models is the lack of generalizability and interpretability. The ML community is increasingly working on bridging this gap. Prominent among them are methods that study causal significance of features, with techniques such as Average Causal Effect (ACE). In this paper, our objective is to utilize the causal analysis framework to measure the significance level of the features in binary classification task.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views