
- Read more about Are Soft Prompts Good Zero-shot Learners for Speech Recognition?
- Log in to post comments
Large self-supervised pre-trained speech models require computationally expensive fine-tuning for downstream tasks. Soft prompt tuning offers a simple parameter-efficient alternative by utilizing minimal soft prompt guidance, enhancing portability while also maintaining competitive performance. However, not many people understand how and why this is so. In this study, we aim to deepen our understanding of this emerging method by investigating the role of soft prompts in automatic speech recognition (ASR).
prompts2.pptx
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about State-Augmented Information Routing in Communication Systems with Graph Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of routing network packets in a large-scale communication system where the nodes have access to only local information. We formulate this problem as a constrained learning problem, which can be solved using a distributed optimization algorithm. We approach this distributed optimization using a novel state-augmentation (SA) strategy to maximize the aggregate information packets at different source nodes, leveraging dual variables corresponding to flow constraint violations.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Inducing Inductive Bias in Vision Transformer for EEG Classification
- Log in to post comments
Human brain signals are highly complex and dynamic in nature. Electroencephalogram (EEG) devices capture some of this complexity, both in space and in time, with a certain resolution. Recently, transformer-based models have been explored in various applications with different modalities of data. In this work, we introduce a transformer-based model for the classification of EEG signals, inspired by the recent success of the Vision Transformer (ViT) in image classification.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about UNLOCKING DEEP LEARNING: A BP-FREE APPROACH FOR PARALLEL BLOCK-WISE TRAINING OF NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Backpropagation (BP) has been a successful optimization technique for deep learning models. However, its limitations, such as backward- and update-locking, and its biological implausibility, hinder the concurrent updating of layers and do not mimic the local learning processes observed in the human brain. To address these issues, recent research has suggested using local error signals to asynchronously train network blocks. However, this approach often involves extensive trial-and-error iterations to determine the best configuration for local training.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Patient-Specific Modeling of Daily Activity Patterns for Unsupervised Detection of Psychotic and Non-Psychotic Relapses
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present our submission to the 2nd e-Prevention Grand Challenge hosted at ICASSP 2024. The objective posed in the challenge was to identify psychotic and non- psychotic relapses in patients using biosignals captured by wearable sensors. Our proposed solution is an unsupervised anomaly detection approach based on Transformers. We train individual models for each patient to predict the timestamps of biosignal measurements on non-relapse days, implicitly modeling normal daily routines.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views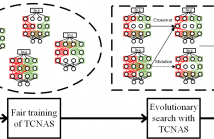
- Read more about TCNAS: TRANSFORMER ARCHITECTURE EVOLVING IN CODE CLONE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Code clone detection aims at finding code fragments with syntactic or semantic similarity. Most of current approaches mainly focus on detecting syntactic similarity while ignoring semantic long-term context alignment, and these detection methods encode the source code using human-designed models, a process which requires both expert input and a significant cost of time for experimentation and refinement. To address these challenges, we introduce the Transformer Code Neural Architecture Search (TCNAS), an approach designed to optimize transformer-based architectures for detection.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views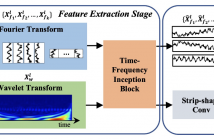
- Read more about WFTNet: Exploiting Global and Local Periodicity in Long-term Time Series Forecasting
- Log in to post comments
Recent CNN and Transformer-based models tried to utilize frequency and periodicity information for long-term time series forecasting. However, most existing work is based on Fourier transform, which cannot capture fine-grained and local frequency structure. In this paper, we propose a Wavelet-Fourier Transform Network (WFTNet) for long-term time series forecasting.
WFTNet.pdf
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views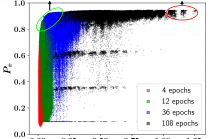
- Read more about EC-NAS: Energy Consumption Aware Tabular Benchmarks for Neural Architecture Search
- Log in to post comments
Energy consumption from the selection, training, and deployment of deep learning models has seen a significant uptick recently. This work aims to facilitate the design of energy-efficient deep learning models that require less computational resources and prioritize environmental sustainability by focusing on the energy consumption. Neural architecture search (NAS) benefits from tabular benchmarks, which evaluate NAS strategies cost-effectively through precomputed performance statistics. We advocate for including energy efficiency as an additional performance criterion in NAS.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about 1-D Spatial Attention in Binarized Convolutional Neural Networks
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a structure called SPBNet for enhancing binarized convolutional neural networks (BCNNs) using a low-cost 1-D spatial attention structure. Attention blocks can compensate for the performance drop in BCNNs. However, the hardware overhead of complex attention blocks can be a significant burden in BCNNs. The proposed attention block consists of low-cost 1-D height-wise and width-wise 1-D convolutions, It has the attention bias to adjust the effects of attended features in ×0.5 − ×1.5.
- Categories:
 155 Views
155 Views
The event camera's low power consumption and ability to capture microsecond brightness changes make it attractive for various computer vision tasks. Existing event representation methods typically convert events into frames, voxel grids, or spikes for deep neural networks (DNNs). However, these approaches often sacrifice temporal granularity or require specialized devices for processing. This work introduces a novel token-based event representation, where each event is considered a fundamental processing unit termed an event-token.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views