
- Read more about High-Accuracy Automatic Person Segmentation with Novel Spatial Saliency Map
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a person segmentation system that achieves high segmentation accuracy with a much smaller CNN network. In this approach, key-point detection annotation is incorporated for the first time and a novel spatial saliency map, in which the intensity of each pixel indicates the likelihood of forming a part of the human and reflects the distance from the body, is generated to provide more spatial information.
- Categories:
 77 Views
77 Views
- Read more about BODYFITR: Robust automatic 3D human body fitting
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes BODYFITR, a fully automatic method to fit a human body model to static 3D scans with complex poses. Automatic and reliable 3D human body fitting is necessary for many applications related to healthcare, digital ergonomics, avatar creation and security, especially in industrial contexts for large-scale product design. Existing works either make prior assumptions on the pose, require manual annotation of the data or have difficulty handling complex poses.
- Categories:
 130 Views
130 Views
- Read more about MULTIPLE INSTANCE DENSE CONNECTED CONVOLUTION NEURAL NETWORK FOR AERIAL IMAGE SCENE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
With the development of deep learning, many state-of-the-art natural image scene classification methods have demonstrated impressive performance. While the current convolution neural network tends to extract global features and global semantic information in a scene, the geo-spatial objects can be located at anywhere in an aerial image scene and their spatial arrangement tends to be more complicated. One possible solution is to preserve more local semantic information and enhance feature propagation.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Multi-Label Zero-Shot Learning With Transfer-Aware Label Embedding Projection
- Log in to post comments
Zero-Shot learning (ZSL) recently has drawn a lot of attention due to its ability to transfer knowledge from seen classes to novel unseen classes, which greatly reduces human labor of labelling data for building new classifiers. Much effort on ZSL however has focused on the standard multi-class setting, the more challenging multi-label zero-shot problem has received limited attention. In this paper, we propose a transfer-aware embedding projection approach to tackle multi-label zero-shot learning.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Graph Signal Sampling via Reinforcement Learning
- Log in to post comments
We model the sampling and recovery of clustered graph signals as a reinforcement learning (RL) problem. The signal sampling is carried out by an agent which crawls over the graph and selects the most relevant graph nodes to sample. The goal of the agent is to select signal samples which allow for the most accurate recovery. The sample selection is formulated as a multi-armed bandit (MAB) problem, which lends naturally to learning efficient sampling strategies using the well-known gradient MAB algorithm.
- Categories:
 115 Views
115 Views
- Read more about FAST COMPRESSIVE SENSING RECOVERY USING GENERATIVE MODELS WITH STRUCTURED LATENT VARIABLES
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning models have significantly improved the visual quality and accuracy on compressive sensing recovery. In this paper, we propose an algorithm for signal reconstruction from compressed measurements with image priors captured by a generative model. We search and constrain on latent variable space to make the method stable when the number of compressed measurements is extremely limited. We show that, by exploiting certain structures of the latent variables, the proposed method produces improved reconstruction accuracy and preserves realistic and non-smooth features in the image.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views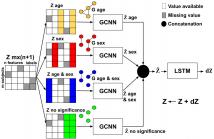
- Read more about Multiple-Graph Recurrent Graph Convolutional Neural Network architectures for predicting disease outcomes
- Log in to post comments
Improving disease outcome prediction can greatly aid in the strategic deployment of secondary prevention approaches. We develop a method to predict the evolution of diseases by taking into account personal attributes of the subjects and their relationships with medical examination results. Our approach builds upon a recent formulation of this problem as a graph-based geometric matrix completion task. The primary innovation is the introduction of multiple graphs, each relying on a different combination of subject attributes.
- Categories:
 162 Views
162 Views
- Read more about MATRIX COMPLETION WITH VARIATIONAL GRAPH AUTOENCODERS: APPLICATION IN HYPERLOCAL AIR QUALITY INFERENCE
- Log in to post comments
Inferring air quality from a limited number of observations is an essential task for monitoring and controlling air pollution. Existing inference methods typically use low spatial resolution data collected by fixed monitoring stations and infer the concentration of air pollutants using additional types of data, e.g., meteorological and traffic information. In this work, we focus on street-level air quality inference by utilizing data collected by mobile stations.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about [Slides] Accelerating Iterative Hard Thresholding for Low-rank Matrix Completion via Adaptive Restart
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces the use of adaptive restart to accelerate iterative hard thresholding (IHT) for low-rank matrix completion. First, we analyze the local convergence of accelerated IHT in the non-convex setting of matrix completion problem (MCP). We prove the linear convergence rate of the accelerated algorithm inside the region near the solution. Our analysis poses a major challenge to parameter selection for accelerated IHT when no prior knowledge of the "local Hessian condition number" is given.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about [Poster] Local Convergence of the Heavy Ball method in Iterative Hard Thresholding for Low-Rank Matrix Completion
- Log in to post comments
We present a momentum-based accelerated iterative hard thresholding (IHT) for low-rank matrix completion. We analyze the convergence of the proposed Heavy Ball (HB) accelerated IHT near the solution and provide optimal step size parameters that guarantee the fastest rate of convergence. Since the optimal step sizes depend on the unknown structure of the solution matrix, we further propose a heuristic for parameter selection that is inspired by recent results in random matrix theory.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views