
- Read more about Content Placement Learning For Success Probability Maximization In Wireless Edge Caching Networks
- Log in to post comments
To meet increasing demands of wireless multimedia communications, caching of important contents in advance is one of the key solutions. Optimal caching depends on content popularity in future which is unknown in advance. In this paper, modeling content popularity as a finite state Markov chain, reinforcement Q-learning is employed to learn optimal content placement strategy in homogeneous Poisson point process (PPP) distributed caching network.
posterq2.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Generalized Boundary Detection Using Compression-Based Analytics
- Log in to post comments
We present a new method for boundary detection within sequential data using compression-based analytics. Our approach is to approximate the information distance between two adjacent sliding windows within the sequence. Large values in the distance metric are indicative of boundary locations. A new algorithm is developed, referred to as sliding information distance (SLID), that provides a fast, accurate, and robust approximation to the normalized information distance. A modified smoothed z-score algorithm is used to locate peaks in the distance metric, indicating boundary locations.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about DISTRIBUTED DIFFERENTIALLY-PRIVATE CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a distributed differentially-private canonical correlation analysis (CCA) algorithm to use on multi-view data. CCA finds a subspace for each view such that projecting the views onto these subspaces simultaneously reduces the dimension and maximizes correlation. In applications involving privacy-sensitive data, such as medical imaging, distributed privacy-preserving algorithms can let data holders maintain local control of their data while participating in joint computations with other data holders.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about CODING TREE EARLY TERMINATION FOR FAST HEVC TRANSRATING BASED ON RANDOM FORESTS
- Log in to post comments
Video transrating has become an essential task in streaming service providers that need to transmit and deliver different versions of the same content for a multitude of users that operate under different network conditions. As the transrating operation is comprised of a decoding and an encoding step in sequence, a huge computational cost is required in such large-scale services, especially when considering the use of complex state-of-the-art codecs, such as the High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Compressing Unstructured Mesh Data Using Spline Fits, Compressed Sensing, and Regression Methods
- Log in to post comments
Compressing unstructured mesh data from computer simulations poses several challenges that are not encountered in the compression of images or videos. Since the spatial locations of the points are not on a regular grid, as in an image, it is difficult to identify near neighbors of a point whose values can be exploited for compression.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Self-Supervised Anomaly Detection for Narrowband SETI Presentation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about RANDOM ENSEMBLE OF LOCALLY OPTIMUM DETECTORS FOR DETECTION OF ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLES
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views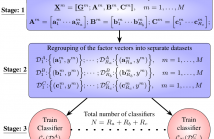
- Read more about Tensor Ensemble Learning
- Log in to post comments
In big data applications, classical ensemble learning is typically infeasible on the raw input data and dimensionality reduction techniques are necessary. To this end, novel framework that generalises classic flat-view ensemble learning to multidimensional tensor- valued data is introduced. This is achieved by virtue of tensor decompositions, whereby the proposed method, referred to as tensor ensemble learning (TEL), decomposes every input data sample into multiple factors which allows for a flexibility in the choice of multiple learning algorithms in order to improve test performance.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Backdoor Attacks on Neural Network Operations
- Log in to post comments
Machine learning is a rapidly growing field that has been expanding into various aspects of technology and science in recent years. Unfortunately, it has been shown recently that machine learning models are highly vulnerable to well-crafted adversarial attacks. This paper develops a novel method for maliciously inserting a backdoor into a well-trained neural network causing misclassification that is only active under rare input keys.
- Categories:
 199 Views
199 Views
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views