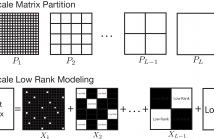
- Read more about Poster for Beyond Low Rank + Sparse: Multi-scale Low Rank Matrix Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views- Read more about ON THE DETECTION OF NON-STATIONARY SIGNALS IN THE MATCHED SIGNAL TRANSFORM DOMAIN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views- Read more about Non-linear regression for bivariate self-similarity identification - application to anomaly detection in Internet traffic based on a joint scaling analysis of packet and byte counts
- Log in to post comments
Internet traffic monitoring is a crucial task for network security. Self-similarity, a key property for a relevant description of internet traffic statistics, has already been massively and successfully involved in anomaly detection. Self-similar analysis was however so far applied either to byte or Packet count time series independently, while both signals are jointly collected and technically deeply related. The present contribution elaborates on a recently proposed multivariate self-similar model, Operator fractional Brownian Motion (OfBm), to
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views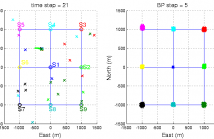
- Read more about Distributed Estimation of Latent Parameters in State Space Models Using Separable Likelihoods
- Log in to post comments
This work is a part of our research on scalable and/or distributed fusion and sensor calibration. We address parameter estimation in multi-sensor state space models which underpins surveillance applications with sensor networks. The parameter likelihood of the problem involves centralised Bayesian filtering of multi-sensor data, which lacks scalability with the number of sensors and induces a large communication load. We propose separable likelihoods which approximate the centralised likelihood with single sensor filtering terms.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views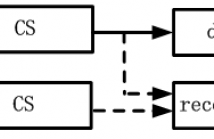
- Read more about Infrared Small Target Detection with Compressive Measurements
- Log in to post comments
A novel scheme for infrared small target detection in compressive domain is presented. First, the original image is separated into two components, i.e., the target and the background. Next, we compress them individually. Finally, the compressed target image is utilized to construct the corresponding compressive detector to perform detection in compressive domain.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about ON THE NULL SPACE CONSTANT FOR LP MINIMIZATION
- Log in to post comments
poster_clm.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Recursive versions of the Levenberg-Marquardt reassigned spectrogram and of the synchrosqueezed
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Estimating parameters in noisy low frequency exponentially damped sinusoids and exponentials
- Log in to post comments
There has been much recent interest in damped sinusoidal models, probably as a result of their relevance to magnetic resonance imaging. In \cite{about2010}, a model which allowed the sinusoid to decay to $0$ was examined, and a Fourier coefficient estimation procedure was proposed.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views- Read more about COHERENCE REGULARIZED DICTIONARY LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views