
- Read more about PhaseSplit: A Variable Splitting Framework for Phase Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
We develop two techniques based on alternating minimization and
alternating directions method of multipliers for phase retrieval (PR)
by employing a variable-splitting approach in a maximum likelihood
estimation framework. This leads to an additional equality constraint,
which is incorporated in the optimization framework using a
quadratic penalty. Both algorithms are iterative, wherein the updates
are computed in closed-form. Experimental results show that: (i)
the proposed techniques converge faster than the state-of-the-art PR
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
Uncertainty principles in finite dimensional vector space have been studied extensively, however they cannot be applied to sparse representation of rational functions. This paper considers the sparse representation for a rational function under a pair of orthonormal rational function bases. We prove the uncertainty principle concerning pairs of compressible representation of rational functions in the infinite dimensional function space. The uniqueness of compressible representation using such pairs is provided as a direct consequence of uncertainty principle.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views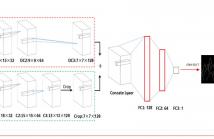
- Read more about SINGLE DEPTH IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose single depth image super-resolution using convolutional neural networks (CNN). We adopt CNN to acquire a high-quality edge map from the input low-resolution (LR) depth image. We use the high-quality edge map as the weight of the regularization term in a total variation (TV) model for super-resolution. First, we interpolate the LR depth image using bicubic interpolation and extract its low-quality edge map. Then, we get the high-quality edge map from the low-quality one using CNN.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
Estimating envelope of a signal has various applications including empirical mode decomposition (EMD) in which the cubic $C^2$-spline based envelope estimation is generally used. While such functional approach can easily control smoothness of an estimated envelope, the so-called undershoot problem often occurs that violates the basic requirement of envelope. In this paper, a tangentially constrained spline with tangential points optimization is proposed for avoiding the undershoot problem while maintaining smoothness.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views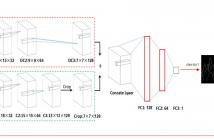
- Read more about SINGLE DEPTH IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION USING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, a novel framework for the single depth image superresolution is proposed. In our framework, we first extract a low-quality edge map from an interpolated depth map.Then we transform the low-quality edge map to a high quality one by our trained deep convolution neural network (CNN) with two-step postprocessing. Guided by the high-quality edge map, we finally utilize a total variation (TV) based model to upsample the initial depth map.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Improved Noise Characterization for Relative Impulse Response Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Relative Impulse Responses (ReIRs) have several applications in speech enhancement, noise suppression and source localization for multi-channel speech processing in reverberant environments. Noise is usually assumed to be white Gaussian during the estimation of the ReIR between two microphones. We show that the noise in this system identification problem is instead dependent upon the microphone measurements and the ReIR itself.
ICASSP_V3.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about ADAPTIVE STFT WITH CHIRP-MODULATED GAUSSIAN WINDOW
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose an adaptive STFT (ASTFT) with adaptive chirp-modulated Gaussian window. The window is obtained from rotating Gaussian function in time-frequency plane by fractional Fourier transform (FRFT). It is completely adaptive where the two parameters, FRFT rotation angle and Gaussian variance, are signal-dependent. The angle dependents on the chirp rate of the signal. The variance is determined by the chirp rate and its first derivative.
- Categories:
 92 Views
92 Views
- Read more about Convolutional group-sparse coding and source localization - Poster
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a new interpretation of non-negatively constrained convolutional coding problems as blind deconvolution problems with spatially variant point spread function. In this light, we propose an optimization framework that generalizes our previous work on non-negative group sparsity for convolutional models. We then link these concepts to source localization problems that arise in scientific imaging, and provide a visual example on an image derived from data captured by the Hubble telescope.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about Sparse overcomplete denoising: aggregation versus global optimization
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views