
- Read more about DISJUNCT MATRICES FOR COMPRESSED SENSING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views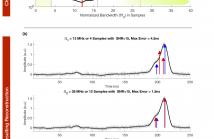
- Read more about Rethinking Super-resolution: The Bandwidth Selection Problem
- Log in to post comments
Super-resolution is the art of recovering spikes from their low-pass projections. Over the last decade specifically, several significant advancements linked with mathematical guarantees and recovery algorithms have been made. Most super-resolution algorithms rely on a two-step procedure: deconvolution followed by high-resolution frequency estimation. However, for this to work, exact bandwidth of low-pass filter must be known; an assumption that is central to the mathematical model of super-resolution.
AB_ICASSP 2019.pdf
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views
- Read more about Tropical Modeling of Weighted Transducer Algorithms on Graphs
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Second order sequential best rotation algorithm with Householder reduction for polynomial matrix eigenvalue decomposition
- Log in to post comments
The Second-order Sequential Best Rotation (SBR2) algorithm, used for Eigenvalue Decomposition (EVD) on para-Hermitian polynomial matrices typically encountered in wideband signal processing applications like multichannel Wiener filtering and channel coding, involves a series of delay and rotation operations to achieve diagonalisation. In this paper, we proposed the use of Householder transformations to reduce polynomial matrices to tridiagonal form before zeroing the dominant element with rotation.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
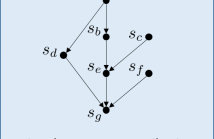
- Read more about A DISCRETE SIGNAL PROCESSING FRAMEWORK FOR MEET/JOIN LATTICES WITH APPLICATIONS TO HYPERGRAPHS AND TREES
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel discrete signal processing framework, called discrete-lattice SP, for signals indexed by a finite lattice. A lattice is a partially ordered set that supports a meet (or join) operation that returns the greatest element below two given elements. Discrete-lattice SP chooses the meet as shift operation and derives associated notion of (meet-invariant) convolution, Fourier transform, frequency response, and a convolution theorem. Examples of lattices include sets of sets that are closed under intersection and trees.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about On the Sensitivity of Spectral Initialization for Noisy Phase Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
The spectral method is an important approach for signal esti- mation that is often used as an initialization to iterative methods as well as a stand-alone estimator, where the signal is estimated by the top eigenvector of certain carefully-constructed data matrix. A re- cent line of work has characterized the asymptotic behavior of such data matrices used in spectral methods, which reveals an interesting phase transition phenomenon: there exists a critical sampling thresh- old below which the estimate of the spectral method is uninforma- tive.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Squared-Loss Mutual Information via High-Dimension Coherence Matrix Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Squared-loss mutual information (SMI) is a surrogate of Shannon mutual information that is more advantageous for estimation. On the other hand, the coherence matrix of a pair of random vectors, a power-normalized version of the sample cross-covariance matrix, is a well-known second-order statistic found in the core of fundamental signal processing problems, such as canonical correlation analysis (CCA).
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about On the Fourier Representation of Computable Continuous Signals
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Toward Robust Interpretable Human Movement Pattern Analysis in a Workplace Setting
- Log in to post comments
Gaining a better understanding of how people move about and interact with their environment is an important piece of understanding human behavior. Careful analysis of individuals’ deviations or variations in movement over time can provide an awareness about changes to their physical or mental state and may be helpful in tracking performance and well-being especially in workplace settings. We propose a technique for clustering and discovering patterns in human movement data by extracting motifs from the time series of durations where participants linger at different locations.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views