- Signal and System Modeling, Representation and Estimation
- Multirate Signal Processing
- Sampling and Reconstruction
- Nonlinear Systems and Signal Processing
- Filter Design
- Adaptive Signal Processing
- Statistical Signal Processing
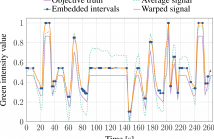
- Read more about A Novel Method for Human Bias Correction of Continuous-time Annotations
- Log in to post comments
Human annotations are of integral value in human behavior studies and in particular for the generation of ground truth for behavior prediction using various machine learning methods. These often subjective human annotations are especially required for studies involving measuring and predicting hidden mental states (e.g. emotions) that cannot effectively be measured or assessed by other means. Human annotations are noisy and prone to the influence of several factors including personal bias, task ambiguity, environmental distractions, and health state.
- Categories:
 93 Views
93 Views
- Read more about FASTER AND STILL SAFE: COMBINING SCREENING TECHNIQUES AND STRUCTURED DICTIONARIES TO ACCELERATE THE LASSO
- Log in to post comments
Accelerating the solution of the Lasso problem becomes crucial when scaling to very high dimensional data.
In this paper, we propose a way to combine two existing acceleration techniques: safe screening tests, which simplify the problem by eliminating useless dictionary atoms; and the use of structured dictionaries which are faster to operate with. A structured approximation of the true dictionary is used at the initial stage of the optimization, and we show how to define screening tests which are still safe despite the approximation error.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Sparse Support Recovery via Covariance Estimation
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of recovering the common support of a set of
$k$-sparse signals $\{\mathbf{x}_{i}\}_{i=1}^{L}$ from noisy linear
underdetermined measurements of the form
$\{{\Phi} \mathbf{x}_{i}+\mathbf{w}_{i}\}_{i=1}^{L}$ where
${\Phi}\in\rr^{m\times N}$ $(m<N)$ is the sensing matrix and
$\mathbf{w}_{i}$ is the additive noise. We employ a Bayesian setup where we impose a Gaussian prior with zero mean and a
common diagonal covariance matrix $\mathbf{\Gamma}$ across all
icassp_v3.pdf
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views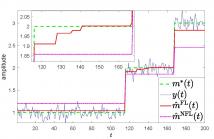
- Read more about CONSISTENT CHANGE POINT DETECTION FOR PIECEWISE CONSTANT SIGNALS WITH NORMALIZED FUSED LASSO
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
The mutual interference between similar radar systems can result in reduced radar sensitivity and increased false alarm rates.
To address the interference mitigation problems in similar radar systems, we propose herein two slow-time coding schemes to modulate the pulses within a coherent processing interval (CPI).
The incorporation of the coding schemes only requires slight modification of the existing systems.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
- Read more about UNEQUAL ERROR PROTECTION QUERYING POLICIES FOR THE NOISY 20 QUESTIONS PROBLEM
- Log in to post comments
We propose a non-adaptive unequal error protection (UEP) querying policy based on superposition coding for the noisy 20 questions problem.
In this problem, a player wishes to successively refine an estimate of the value of a continuous random variable by posing binary queries and receiving noisy responses.
When the queries are designed non-adaptively as a single block and the noisy responses are modeled as the outputs of a binary symmetric channel the 20 questions problem can be mapped to an equivalent problem of channel coding with UEP.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about RECOVERING SIGNALS FROM THEIR FROG TRACE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about ROBUST OBJECT-AWARE SAMPLE CONSENSUS WITH APPLICATION TO LIDAR ODOMETRY
- Log in to post comments
Random sample consensus (RANSAC) is a popular paradigm for parameter estimation with outlier detection, which plays an essential role in 3D robot vision, especially for LiDAR odometry. The success of RANSAC strongly depends on the probability of selecting a subset of pure inliers, which sets barriers to robust and fast parameter estimation. Although significant efforts have been made to improve RANSAC in various scenarios, its strong dependency on inlier selection is still a problem.
海报0411晚修改.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views