- Signal and System Modeling, Representation and Estimation
- Multirate Signal Processing
- Sampling and Reconstruction
- Nonlinear Systems and Signal Processing
- Filter Design
- Adaptive Signal Processing
- Statistical Signal Processing
- Read more about SUPERPIXEL-GUIDED CFAR DETECTION OF SHIPS AT SEA IN SAR IMAGERY
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about Online Empirical Mode Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
The success of Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) resides in its practical approach to dissect non-stationary data. EMD repetitively goes through the entire data span to iteratively extract Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMFs). This approach, however, is not suitable for data stream as the entire data set has to be reconsidered every time a new point is added. To overcome this, we propose Online EMD, an algorithm that extracts IMFs on the fly.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views

- Read more about Tracking Time-Vertex Propagation using Dynamic Graph Wavelets
- Log in to post comments
Graph Signal Processing generalizes classical signal processing to signal or data indexed by the vertices of a weighted graph. So far, the research efforts have been focused on static graph signals. However numerous applications involve graph signals evolving in time, such as spreading or propagation of waves on a network. The analysis of this type of data requires a new set of methods that takes into account the time and graph dimensions. We propose a novel class of wavelet frames named Dynamic Graph Wavelets, whose time-vertex evolution follows a dynamic process.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Rethinking Sketching as Sampling: Efficient Approximate Solution to Linear Inverse Problems
- Log in to post comments
Sampling and reconstruction of bandlimited graph signals have well-appreciated merits for dimensionality reduction, affordable storage, and online processing of streaming network data. However, these parsimonious signals are oftentimes encountered with high-dimensional linear inverse problems. Hence, interest shifts from reconstructing the signal itself towards instead approximating the input to a prescribed linear operator efficiently.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Neighborhood-Preserving Translations on Graphs
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about MORPHOLOGICAL PDES ON GRAPHS FOR ANALYZING UNORGANIZED DATA IN 3D AND HIGHER
- Log in to post comments
globalsip.pdf
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views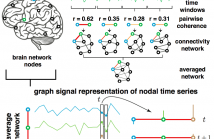
- Read more about Graph Frequency Analysis of Brain Signals
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents methods to analyze functional brain networks and signals from graph spectral perspectives. The notion of frequency and filters traditionally defined for signals supported on regular domains such as discrete time and image grids has been recently generalized to irregular graph domains, and defines brain graph frequencies associated with different levels of spatial smoothness across the brain regions. Brain network frequency also enables the decomposition of brain signals into pieces corresponding to smooth or rapid variations.
- Categories:
 127 Views
127 Views
- Read more about IEEE SP Cup 2016 Project Report by Team "10Hertz": Exploring Power Signals for Location Forensics of Media Recordings
- Log in to post comments
Electric Network Frequency is the frequency of power distribution networks in power grids that fluctuates about a nominal value with respect to the changing loads.Its ubiquitous nature has made notable contributions to forensic analysis that has substantiated its use as a significant tool in this area. In this paper we have proposed a technique to identify the power grid in which the ENF containing signal was recorded, without the assistance of concurrent power references.
- Categories:
 125 Views
125 Views
- Read more about A HIGH PERFORMANCE BASEBAND INSTRUMENT
- Log in to post comments
Testing complex digital signal processors (DSPs) requires a development platform with sufficient
signal bandwidth and system performance to fully exercise the DSP. Without a development plat-
form, verification of DSPs would be limited to monitoring test output signals for an indication of
performance and successful operation. In addition, a development platform with high-speed analog
input and output interfaces to the DSP system allows it to be used directly in many sophisticated
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views