
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2020 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Efficient Multichannel Nonlinear Acoustic Echo Cancellation Based On A Cooperative Strategy
- Log in to post comments
While a common approach to address nonlinear distortions, emitted by multiple loudspeakers and observed by multiple microphones, is to use post-filtering techniques, this paper proposes a cooperative strategy to rather model and then cancel such distortions. In this approach, the overall problem of modeling distortions emitted by a number of loudspeakers is divided into multiple simpler and easier tasks of estimating distortions emitted by subsets of loudspeakers.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views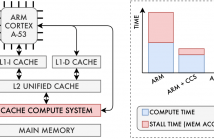
- Read more about PROCESSING CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS ON CACHE
- Log in to post comments
With the advent of Big Data application domains, several Machine Learning (ML) signal-processing algorithms such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are required to process progressively larger datasets at a great cost in terms of both compute power and memory bandwidth. Although dedicated accelerators have been developed targeting this issue, they usually require moving massive amounts of data across the memory hierarchy to the processing cores and low-level knowledge of how data is stored in the memory devices to enable in-/near-memory processing solutions.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
We propose a computational framework for ranking images (group photos in particular) taken at the same event within a short time span. The ranking is expected to correspond with human perception of overall appeal of the images. We hypothesize and provide evidence through subjective analysis that the factors that appeal to humans are its emotional content, aesthetics and image quality. We propose a network which is an ensemble of three information channels, each predicting a score corresponding to one of the three visual appeal factors.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views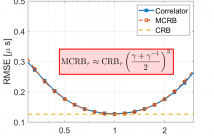
- Read more about Misspecified Cramer-Rao Bound For Delay Estimation With A Mismatched Waveform: A Case Study
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we investigate the problem of time of arrival estimation which occurs in many real-world applications, such as indoor localization or non-destructive testing via ultrasound or radar. A problem that is often overlooked when analyzing these systems is that in practice, we will typically not have exact information about the pulse shape. Therefore, there may be a mismatch between the parametric model that is assumed to derive and study the estimators versus the real model we find in practice.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views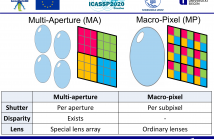
- Read more about Single-Shot Real-Time Multiple-Path Time-of-Flight Depth Imaging for Multi-Aperture and Macro-Pixel Sensors
- Log in to post comments
Multiple-Path Interference (MPI) is a major drawback of Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors. MPI occurs when a ToF pixel receives more than a single light bounce from the scene. Current methods resolving more than a single return per pixel rely on the sequential acquisition of large amounts of data and are too computationally expensive to deliver depth images in real time. These factors have precluded the development of a multiple-path ToF camera to date. In this work we consider two hardware alternatives that can be used to acquire all necessary raw data in a single shot.
- Categories:
 117 Views
117 Views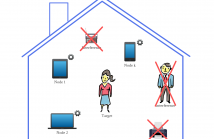
- Read more about DNN-BASED DISTRIBUTED MULTICHANNEL MASK ESTIMATION FOR SPEECH ENHANCEMENT IN MICROPHONE ARRAYS
- Log in to post comments
Multichannel processing is widely used for speech enhancement but several limitations appear when trying to deploy these solutions in the real world. Distributed sensor arrays that consider several devices with a few microphones is a viable solution which allows for exploiting the multiple devices equipped with microphones that we are using in our everyday life. In this context, we propose to extend the distributed adaptive node-specific signal estimation approach to a neural network framework.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views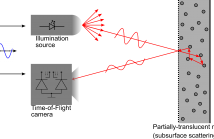
- Read more about A Single-Wavelength Real-Time Material-Sensing Camera Based on Time-of-Flight Measurements
- Log in to post comments
Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras provide a fast and robust way of acquiring the 3D shape of real scenes. Dense depth images can be generated at tens of frame per second. 3D shapes can be then segmented and objects classified, but can we directly sense the objects’ material using just a ToF camera? This live demonstration proves the answer to be affirmative. This possibility has only very recently been unveiled and we are, to the best of our knowledge, the first providing a live demonstrator showing the feasibility of this approach.
- Categories:
 158 Views
158 Views
- Read more about EXTENDED CYCLIC COORDINATE DESCENT FOR ROBUST ROW-SPARSE SIGNAL RECONSTRUCTION IN THE PRESENCE OF OUTLIERS
- Log in to post comments
The problem of row-sparse signal reconstruction for complex-valued data with outliers is investigated in this paper. First, we formulate the problem by taking advantage of a sparse weight matrix, which is used to down-weight the outliers. The formulated problem belongs to LASSO-type problems, and such problems can be efficiently solved via cyclic coordinate descent (CCD). We propose an extended CCD algorithm to solve the problem for complex-valued measurements, which requires careful characterization and derivation.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about Regularized partial phase synchrony index applied to dynamical functional connectivity estimation
- Log in to post comments
We study the inference of conditional independence graph from the partial Phase Locking Value (PLV) index of multivariate time series. A typical application is the inference of temporal functional connectivity from brain data. We extend the recently proposed time-varying graphical lasso to the measurement of partial locking values, yielding a sparse and temporally coherent dynamical graph that characterizes the evolution of the phase synchrony between each pair of signals.
PPFrusque.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation with Symmetric Adaptation Consistency
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised domain adaptation, which leverages label information from other domains to solve tasks on a domain without any labels, can alleviate the problem of the scarcity of labels and expensive labeling costs faced by supervised semantic segmentation. In this paper, we utilize adversarial learning and semi-supervised learning simultaneously to solve the task of unsupervised domain adaptation in semantic segmentation.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views