
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2020 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views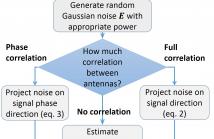
- Read more about Theoretical Performance Bound of Uplink Channel Estimation Accuracy in Massive MIMO
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a new performance bound for uplink channel estimation (CE) accuracy in the Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) system. The proposed approach is based on noise power calculation after the CE unit in a multi-antenna receiver. Each time the impulse response of ideal channel estimation is decomposed into separate taps (beams) and cross-covariance matrix is calculated between them.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Multitask Learning with Capsule Networks for Speech-to-Intent Applications
- Log in to post comments
Voice controlled applications can be a great aid to society, especially for physically challenged people. However this requires robustness to all kinds of variations in speech. A spoken language understanding system that learns from interaction with and demonstrations from the user, allows the use of such a system in different settings and for different types of speech, even for deviant or impaired speech, while also allowing the user to choose a phrasing.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views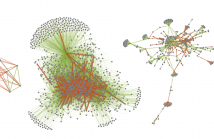
- Read more about LEARNING SIGNED GRAPHS FROM DATA
- Log in to post comments
Signed graphs have recently been found to offer advantages over unsigned graphs in a variety of tasks. However, the problem of learning graph topologies has only been considered for the unsigned case. In this paper, we propose a conceptually simple and flexible approach to signed graph learning via signed smoothness metrics. Learning the graph amounts to solving a convex optimization problem, which we show can be reduced to an efficiently solvable quadratic problem. Applications to signal reconstruction and clustering corroborate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about IMAGE SEGMENTATION BASED PRIVACY-PRESERVING HUMAN ACTION RECOGNITION FOR ANOMALY DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about Multi-Task Learning in Autonomous Driving Scenarios Via Adaptive Feature Refinement Networks
- Log in to post comments
Many deep learning applications benefit from multi-task learning with several related objectives. In autonomous driving scenarios, being able to accurately infer motion and spatial information is essential for scene understanding. In this paper, we combine an adaptive feature refinement module and a unified framework for joint learning of optical flow, depth and camera pose estimation in an unsupervised manner.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views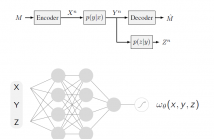
- Read more about Conditional Mutual Information Neural Estimator
- Log in to post comments
Several recent works in communication systems have proposed to leverage the power of neural networks in the design of encoders and decoders. In this approach, these blocks can be tailored to maximize the transmission rate based on aggregated samples from the channel. Motivated by the fact that, in many communication schemes, the achievable transmission rate is determined by a conditional mutual information term, this paper focuses on neural-based estimators for this information-theoretic quantity.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views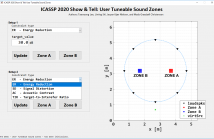
- Read more about User Tuneable Sound Zones
- Log in to post comments
Creating sound zones has been an active area of research since it was first introduced. Generally, this can be done either by maximizing an acoustic contrast that represents the acoustic potential energy ratio between the bright and dark zones or by minimizing a reproduction error between the desired and reproduced sound fields. However, the former suffers from severe distortion in the reproduced sound field, whereas the latter suffers from poor acoustic contrast.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about COLOUR COMPRESSION OF PLENOPTIC POINT CLOUDS USING RAHT-KLT WITH PRIOR COLOUR CLUSTERING AND SPECULAR/DIFFUSE COMPONENT SEPARATION
- Log in to post comments
The recently introduced plenoptic point cloud representation marries a 3D point cloud with a light field. Instead of each point being associated with a single colour value, there can be multiple values to represent the colour at that point as perceived from different viewpoints. This representation was introduced together with a compression technique for the multi-view colour vectors, which is an extension of the RAHT method for point cloud attribute coding.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views