
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about FPGA HARDWARE DESIGN FOR PLENOPTIC 3D IMAGE PROCESSING ALGORITHM TARGETING A MOBILE APPLICATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Error estimate in second-order continuous-time sigma-delta modulators
- Log in to post comments
Continuous-time Sigma-Delta modulators are oversampling Analog-to-Digital converters that may provide higher sampling rates and lower power consumption than their discrete counterpart. Whereas approximation errors are established for high-order discrete time Sigma-Delta modulators, theoretical analysis of the error between the filtered output and the input remain scarce.
poster_1.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
We propose an adapter based multi-domain Transformer based language model (LM) for Transformer ASR. The model consists of a big size common LM and small size adapters. The model can perform multi-domain adaptation with only the small size adapters and its related layers. The proposed model can reuse the full fine-tuned LM which is fine-tuned using all layers of an original model. The proposed LM can be expanded to new domains by adding about 2% of parameters for a first domain and 13% parameters for after second domain.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views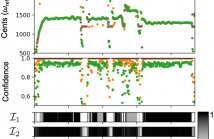
- Read more about RELIABILITY ASSESSMENT OF SINGING VOICE F0-ESTIMATES USING MULTIPLE ALGORITHMS
- Log in to post comments
Over the last decades, various conceptually different approaches for fundamental frequency (F0) estimation in monophonic audio recordings have been developed. The algorithms’ performances vary depending on the acoustical and musical properties of the input audio signal. A common strategy to assess the reliability (correctness) of an estimated F0-trajectory is to evaluate against an annotated reference. However, such annotations may not be available for a particular audio collection and are typically laborintensive to generate.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Meta Ordinal Weighting Net For Improving Lung Nodule Classification
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Learning Bollobás-Riordan Graphs Under Partial Observability - Presentation Slides
- Log in to post comments
This work examines the problem of learning the topology of a network (graph learning) from the signals produced at a subset of the network nodes (partial observability). This challenging problem was recently tackled assuming that the topology is drawn according to an Erdős-Rényi model, for which it was shown that graph learning under partial observability is achievable, exploiting in particular homogeneity across nodes and independence across edges.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Learning Bollobás-Riordan Graphs Under Partial Observability - Poster
- Log in to post comments
This work examines the problem of learning the topology of a network (graph learning) from the signals produced at a subset of the network nodes (partial observability). This challenging problem was recently tackled assuming that the topology is drawn according to an Erdős-Rényi model, for which it was shown that graph learning under partial observability is achievable, exploiting in particular homogeneity across nodes and independence across edges.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views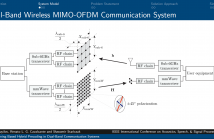
- Read more about DEEP LEARNING BASED HYBRID PRECODING IN DUAL-BAND COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a deep learning-based method that uses spatial and temporal information extracted from the sub-6GHz band to predict/track beams in the millimeter-wave (mmWave) band. In more detail, we consider a dual-band communication system operating in both the sub-6GHz and mmWave bands. The objective is to maximize the achievable mutual information in the mmWave band with a hybrid analog/digital architecture where analog precoders (RF precoders) are taken from a finite codebook.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about LOW-RANK AND SPARSE DECOMPOSITION FOR JOINT DOA ESTIMATION AND CONTAMINATED SENSORS DETECTION WITH SPARSELY CONTAMINATED ARRAYS
- Log in to post comments
Many works have been done in direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation in the presence of sensor gain and phase uncertainties in the past decades. Most of the existing approaches require either auxiliary sources with exactly known DOAs or perfectly partly calibrated arrays. In this work, we consider sparsely contaminated arrays in which only a few sensors are contaminated by sensor gain and phase errors, and moreover, the number of contaminated sensors as well as their positions are unknown.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about INTEGRATED CLASSIFICATION AND LOCALIZATION OF TARGETS USING BAYESIAN FRAMEWORK IN AUTOMOTIVE RADARS
- Log in to post comments
Automatic radar based classification of automotive targets, such as pedestrians and cyclist, poses several challenges due to low inter-class variations among different classes and large intra-class variations. Further, different targets required to track in typical automotive scenario can have completely varying dynamics which gets challenging for tracker using conventional state vectors. Compared to state-of-the-art using independent classification and tracking, in this paper, we propose an integrated tracker and classifier leading to a novel Bayesian framework.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views