
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.
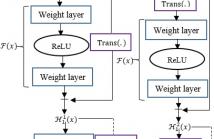
- Read more about BLEND-RES^2NET: Blended Representation Space by Transformation of Residual Mapping with Restrained Learning For Time Series Classification
- Log in to post comments
The typical problem like insufficient training instances in time series classification task demands for novel deep neural architecture to warrant consistent and accurate performance. Deep Residual Network (ResNet) learns through H(x)=F(x)+x, where F(x) is a nonlinear function. We propose Blend-Res2Net that blends two different representation spaces: H^1 (x)=F(x)+Trans(x) and H^2 (x)=F(Trans(x))+x with the intention of learning over richer representation by capturing the temporal as well as the spectral signatures (Trans(∙) represents the transformation function).
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Phoneme based Neural Transducer for Large Vocabulary Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
To join the advantages of classical and end-to-end approaches for speech recognition, we present a simple, novel and competitive approach for phoneme-based neural transducer modeling. Different alignment label topologies are compared and word-end-based phoneme label augmentation is proposed to improve performance. Utilizing the local dependency of phonemes, we adopt a simplified neural network structure and a straightforward integration with the external word-level language model to preserve the consistency of seq-to-seq modeling.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about PositNN: Training Deep Neural Networks with Mixed Low-Precision Posit
- Log in to post comments
Low-precision formats have proven to be an efficient way to reduce not only the memory footprint but also the hardware resources and power consumption of deep learning computations. Under this premise, the posit numerical format appears to be a highly viable substitute for the IEEE floating-point, but its application to neural networks training still requires further research. Some preliminary results have shown that 8-bit (and even smaller) posits may be used for inference and 16-bit for training, while maintaining the model accuracy.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views

- Read more about Exploiting Non-negative Matrix Factorization for Binaural Sound Localization in the Presence of Directional Interference
- Log in to post comments
This study presents a novel solution to the problem of binaural localization of a speaker in the presence of interfering directional noise and reverberation. Using a state-of-the-art binaural localization algorithm based on a deep neural network (DNN), we propose adding a source separation stage based on non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) to improve the localization performance in conditions with interfering sources.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views

- Read more about Autoregressive Fast Multichannel Nonnegative Matrix Factorization For Joint Blind Source Separation And Dereverberation
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes a joint blind source separation and dereverberation method that works adaptively and efficiently in a reverberant noisy environment. The modern approach to blind source separation (BSS) is to formulate a probabilistic model of multichannel mixture signals that consists of a source model representing the time-frequency structures of source spectrograms and a spatial model representing the inter-channel covariance structures of source images.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
In this work, we present a hybrid CTC/Attention model based on a modified ResNet-18 and Convolution-augmented transformer (Conformer), that can be trained in an end-to-end manner. In particular, the audio and visual encoders learn to extract features directly from raw pixels and audio waveforms, respectively, which are then fed to conformers and then fusion takes place via a Multi-Layer Percep- tron (MLP). The model learns to recognise characters using a com- bination of CTC and an attention mechanism.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
Recent work introduced a framework for signal processing (SP) on meet/join lattices. Such a lattice is partially ordered and supports a meet (or join) operation that returns the greatest lower bound and the smallest upper bound of two elements, respectively. Lattices appear in various domains and can be used, for example, to express rankings in social choice theory or multisets in combinatorial auctions. Discrete lattice SP (DLSP) uses the meet operation as shift and derives associated notions of convolution and Fourier transform for signals indexed by lattices.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about The Use of Voice Source Features for Sung Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we ask whether vocal source features (pitch, shimmer, jitter, etc) can improve the performance of automatic sung
3256.pdf
3256 (1).pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views