
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

While globally optimal solutions to many convex programs can be computed efficiently in polynomial time, this is, in general, not possible for nonconvex optimization problems. Therefore, locally optimal approaches or other efficient suboptimal heuristics are usually applied for practical implementations. However, there is also a strong interest in computing globally optimal solutions of nonconvex problems in offline simulations in order to benchmark faster suboptimal algorithms. Global solutions often rely on monotonicity properties.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Multi-Channel Target Speech Extraction with Channel Decorrelation and Target Speaker Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
The end-to-end approaches for single-channel target speech extraction have attracted widespread attention. However, the studies for end-to-end multi-channel target speech extraction are still relatively limited. In this work, we propose two methods for exploiting the multi-channel spatial information to extract the target speech. The first one is using a target speech adaptation layer in a parallel encoder architecture. The second one is designing a channel decorrelation mechanism to extract the inter-channel differential information to enhance the multi-channel encoder representation.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Plug-And-Play Learned Gaussian-mixture Approximate Message Passing
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Globally Optimal Beamforming for Rate Splitting Multiple Access
- Log in to post comments
We consider globally optimal precoder design for rate splitting multiple access in Gaussian multiple-input single-output downlink channels with respect to weighted sum rate and energy efficiency maximization. The proposed algorithm solves an instance of the joint multicast and unicast beamforming problem and includes multicast- and unicast-only beamforming as special cases. Numerical results show that it outperforms state-of-the-art algorithms in terms of numerical stability and converges almost twice as fast.
- Categories:
 108 Views
108 Views
- Read more about Deep Residual Echo Suppression with a Tunable Tradeoff Between Signal Distortion and Echo Suppression
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a residual echo suppression method using a UNet neural network that directly maps the outputs of a linear acoustic echo canceler to the desired signal in the spectral domain. This system embeds a design parameter that allows a tunable tradeoff between the desired-signal distortion and residual echo suppression in double-talk scenarios. The system employs 136 thousand parameters, and requires 1.6 Giga floating-point operations per second and 10 Mega-bytes of memory.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about TIME-DOMAIN CONCENTRATION AND APPROXIMATION OF COMPUTABLE BANDLIMITED SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
Turing computability deals with the question of what is theoretically computable on a digital computer, and hence is relevant whenever digital hardware is used. In this paper we study different possibilities to define computable bandlimited signals and systems. We consider a definition that uses finite Shannon sampling series as approximating functions and another that employs computable continuous functions together with an effectively computable time concentration. We discuss the advantages and drawbacks of both definitions and analyze the connections and differences.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Social Learning Under Inferential Attacks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views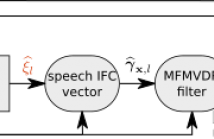
- Read more about Deep Multi-Frame MVDR Filtering for Single-Microphone Speech Enhancement -- Slides
- Log in to post comments
Multi-frame algorithms for single-microphone speech enhancement, e.g., the multi-frame minimum variance distortionless response (MFMVDR) filter, are able to exploit speech correlation across adjacent time frames in the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) domain. Provided that accurate estimates of the required speech interframe correlation vector and the noise correlation matrix are available, it has been shown that the MFMVDR filter yields a substantial noise reduction while hardly introducing any speech distortion.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Deep Multi-Frame MVDR Filtering for Single-Microphone Speech Enhancement -- Poster
- Log in to post comments
Multi-frame algorithms for single-microphone speech enhancement, e.g., the multi-frame minimum variance distortionless response (MFMVDR) filter, are able to exploit speech correlation across adjacent time frames in the short-time Fourier transform (STFT) domain. Provided that accurate estimates of the required speech interframe correlation vector and the noise correlation matrix are available, it has been shown that the MFMVDR filter yields a substantial noise reduction while hardly introducing any speech distortion.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views