
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about STATISTICAL, SPECTRAL AND GRAPH REPRESENTATIONS FOR VIDEO-BASED FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION IN CHILDREN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about STATISTICAL, SPECTRAL AND GRAPH REPRESENTATIONS FOR VIDEO-BASED FACIAL EXPRESSION RECOGNITION IN CHILDREN
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Semi-supervised standardized detection of periodic signals with application to exoplanet detection
- Log in to post comments
We propose a numerical methodology for detecting periodicities in unknown colored noise and for evaluating the ‘significance levels’ (p-values) of the test statistics. The procedure assumes and leverages the existence of a set of time series obtained under the null hypothesis (a null training sample, NTS) and possibly complementary side information. The test statistic is computed from a standardized periodogram, which is a pointwise division of the periodogram of the series under test to an averaged periodogram obtained from the NTS.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views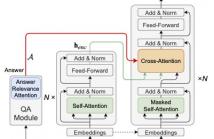
- Read more about QA4QG: USING QUESTION ANSWERING TO CONSTRAIN MULTI-HOP QUESTION GENERATION
- Log in to post comments
Multi-hop question generation (MQG) aims to generate complex questions which require reasoning over multiple pieces of information of the input passage. Most existing work on MQG has focused on exploring graph-based networks to equip the traditional Sequence-to-sequence framework with reasoning ability. However, these models do not take full advantage of the constraint between questions and answers. Furthermore, studies on multi-hop question answering (QA) suggest that Transformers can replace the graph structure for multi-hop reasoning.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views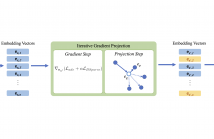
- Read more about BLOCK-SPARSE ADVERSARIAL ATTACK TO FOOL TRANSFORMER-BASED TEXT CLASSIFIERS
- Log in to post comments
Recently, it has been shown that, in spite of the significant performance of deep neural networks in different fields, those are vulnerable to adversarial examples. In this paper, we propose a gradient-based adversarial attack against transformer-based text classifiers. The adversarial perturbation in our method is imposed to be block-sparse so that the resultant adversarial example differs from the original sentence in only a few words. Due to the discrete nature of textual data, we perform gradient projection to find the minimizer of our proposed optimization problem.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about A TEST FOR CONDITIONAL CORRELATION BETWEEN RANDOM VECTORS BASED ON WEIGHTED U-STATISTICS
- Log in to post comments
This article explores U-Statistics as a tool for testing conditional correlation between two multivariate sources with respect to a potential confounder. The proposed approach is effectively an instance of weighted U-Statistics and does not impose any statistical model on the processed data, in contrast to other well-known techniques that assume Gaussianity. By avoiding determinants and inverses, the method presented displays promising robustness in small-sample regimes. Its performance is evaluated numerically through its MSE and ROC curves.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A TEST FOR CONDITIONAL CORRELATION BETWEEN RANDOM VECTORS BASED ON WEIGHTED U-STATISTICS
- Log in to post comments
This article explores U-Statistics as a tool for testing conditional correlation between two multivariate sources with respect to a potential confounder. The proposed approach is effectively an instance of weighted U-Statistics and does not impose any statistical model on the processed data, in contrast to other well-known techniques that assume Gaussianity. By avoiding determinants and inverses, the method presented displays promising robustness in small-sample regimes. Its performance is evaluated numerically through its MSE and ROC curves.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Learning Expanding Graphs for Signal Interpolation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Learning Expanding Graphs for Signal Interpolation
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Semi-Supervised Standardized Detection of Periodic Signals with Application to Exoplanet Detection
- Log in to post comments
We propose a numerical methodology for detecting periodicities in unknown colored noise and for evaluating the ‘significance levels’ (p-values) of the test statistics. The procedure assumes and leverages the existence of a set of time series obtained under the null hypothesis (a null training sample, NTS) and possibly complementary side information. The test statistic is computed from a standardized periodogram, which is a pointwise division of the periodogram of the series under test to an averaged periodogram obtained from the NTS.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views