
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Neural Collapse in Deep Homogeneous Classifiers and the Role of Weight Decay
- Log in to post comments
Neural Collapse is a phenomenon recently discovered in deep classifiers where the last layer activations collapse onto their class means, while the means and last layer weights take on the structure of dual equiangular tight frames. In this paper we present results showing the role of weight decay in the emergence of Neural Collapse in deep homogeneous networks. We show that certain near-interpolating minima of deep networks satisfy the Neural Collapse condition, and this can be derived from the gradient flow on the regularized square loss.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views

- Read more about Stealthy Backdoor Attack With Adversarial Training
- Log in to post comments
Slides.pdf
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Proximal-based adaptive simulated annealing for global optimization (slides)
- Log in to post comments
Simulated annealing (SA) is a widely used approach to solve global optimization problems in signal processing. The initial non-convex problem is recast as the exploration of a sequence of Boltzmann probability distributions, which are increasingly harder to sample from. They are parametrized by a temperature that is iteratively decreased, following the so-called cooling schedule. Convergence results of SA methods usually require the cooling schedule to be set a priori with slow decay. In this work, we introduce a new SA approach that selects the cooling schedule on the fly.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Proximal-based adaptive simulated annealing for global optimization (poster)
- Log in to post comments
Simulated annealing (SA) is a widely used approach to solve global optimization problems in signal processing. The initial non-convex problem is recast as the exploration of a sequence of Boltzmann probability distributions, which are increasingly harder to sample from. They are parametrized by a temperature that is iteratively decreased, following the so-called cooling schedule. Convergence results of SA methods usually require the cooling schedule to be set a priori with slow decay. In this work, we introduce a new SA approach that selects the cooling schedule on the fly.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Exploiting Temporal Context in CNN Based Multisource DOA Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Supervised learning methods are a powerful tool for direction of arrival (DOA) estimation because they can cope with adverse conditions where simplified models fail. In this work, we consider a previously proposed convolutional neural network (CNN) approach that estimates the DOAs for multiple sources from the phase spectra of the microphones. For speech, specifically, the approach was shown to work well even when trained entirely on synthetically generated data. However, as each frame is processed separately, temporal context cannot be taken into account.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about iSTFTNet: Fast and Lightweight Mel-Spectrogram Vocoder Incorporating Inverse Short-Time Fourier Transform
- Log in to post comments
We propose iSTFTNet, which replaces some output-side layers of the mel-spectrogram vocoder with the inverse short-time Fourier transform (iSTFT) after sufficiently reducing the frequency dimension using upsampling layers, reducing the computational cost from black-box modeling and avoiding redundant estimations of high-dimensional spectrograms. During our experiments, we applied our ideas to three HiFi-GAN variants and made the models faster and more lightweight with a reasonable speech quality.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about A KNOWLEDGE/DATA ENHANCED METHOD FOR JOINT EVENT AND TEMP RELATION EXTRACTIONORAL
- Log in to post comments
Understanding temporal relations (TempRels) between events is an important task that could benefit many downstream NLP applications. This task inevitably faces the challenges of both a limited amount of high-quality training data and a very biased distribution of TempRels. These problems will substantially hurt the performance of extraction systems because they are inclined to predict dominant TempRels when training with a limited amount of data.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views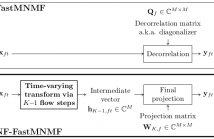
- Read more about Flow-Based Fast Multichannel Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Blind Source Separation
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes a blind source separation method for multichannel audio signals, called NF-FastMNMF, based on the integration of the normalizing flow (NF) into the multichannel nonnegative matrix factorization with jointly-diagonalizable spatial covariance matrices, a.k.a. FastMNMF.
- Categories:
 115 Views
115 Views
- Read more about PEER COLLABORATIVE LEARNING FOR POLYPHONIC SOUND EVENT DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes how semi-supervised learning, called peer collaborative learning (PCL), can be applied to the polyphonic sound event detection (PSED) task, which is one of the tasks in the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events (DCASE) challenge. Many deep learning models have been studied to determine what kind of sound events occur where and for how long in a given audio clip.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views