- Virtual reality and 3D imaging
- Quality Assessment
- Haptic technology and interaction
- Hardware and software for multimedia systems
- Bio-inspired multimedia systems and signal processing
- Multimedia communications and networking
- Multimedia computing systems and applications
- Multimodal signal processing
- Multimedia security and content protection
- Multimedia human-machine interface and interaction
- Multimedia databases and digital libraries
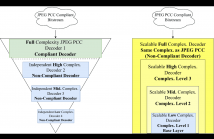
- Read more about Learning-based Point Cloud Decoding With Independent and Scalable Reduced Complexity
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Point Clouds (PCs) have gained significant attention due to their usage in diverse application domains, notably virtual and augmented reality. While PCs excel in providing detailed 3D visualization, this typically requires millions of points which must be efficiently coded for real-world deployment, notably storage and streaming. Recently, learning-based coding solutions have been adopted, notably in the JPEG Pleno Point Coding (PCC) standard, which uses a coding model with millions of model parameters.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about Non-separable Wavelet Transform Using Learnable Convolutional Lifting Steps
- Log in to post comments
Wavelet transforms have been a relevant topic in signal processing for many years. One of the most common strategies when designing wavelet transforms is the use of lifting schemes, known for their perfect reconstruction properties and flexible design. This paper introduces a novel 2D non-separable lifting design methodology based on deep learning architectures. The proposed method is assessed within the context of end-to-end lossless image compression.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about A SOUND APPROACH: Using Large Language Models to generate audio descriptions for egocentric text-audio retrieval - Poster
- Log in to post comments
Video databases from the internet are a valuable source of text-audio retrieval datasets. However, given that sound and vision streams represent different "views" of the data, treating visual descriptions as audio descriptions is far from optimal. Even if audio class labels are present, they commonly are not very detailed, making them unsuited for text-audio retrieval. To exploit relevant audio information from video-text datasets, we introduce a methodology for generating audio-centric descriptions using Large Language Models (LLMs).
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about ColorFlow_ICASSP2024
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Image colorization is an ill-posed task, as objects within grayscale images can correspond to multiple colors, motivating researchers to establish a one-to-many relationship between objects and colors. Previous work mostly could only create an insufficient deterministic relationship. Normalizing flow can fully capture the color diversity from natural image manifold. However, classical flow often overlooks the color correlations between different objects, resulting in generating unrealistic color.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about TALKNCE: IMPROVING ACTIVE SPEAKER DETECTION WITH TALK-AWARE CONTRASTIVE LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
The goal of this work is Active Speaker Detection (ASD), a task to determine whether a person is speaking or not in a series of video frames.
Previous works have dealt with the task by exploring network architectures while learning effective representations has been less explored.
In this work, we propose TalkNCE, a novel talk-aware contrastive loss. The loss is only applied to part of the full segments where a person on the screen is actually speaking.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about A SELF-SUPERVISED LEARNING APPROACH FOR DETECTING NON-PSYCHOTIC RELAPSES USING WEARABLE-BASED DIGITAL PHENOTYPING
- Log in to post comments
We present MagCIL's approach for the 1st track of the "2nd e-Prevention challenge: Psychotic and Non-Psychotic Relapse Detection using Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping". First we present our approach for preprocessing and extracting features from the wearable's raw data. We then propose a Transformer model for learning self-supervised representations from augmented features, trained on data from non-relapse days from each of the 9 patients of the challenge. We adopt two unsupervised methods for detecting relapse days as outliers.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about MLSP-L13.4: Elevating Skeleton-Based Action Recognition with Efficient Multi-Modality Self-Supervision
- Log in to post comments
Self-supervised representation learning for human action recognition has developed rapidly in recent years. Most of the existing works are based on skeleton data while using a multi-modality setup.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views- Read more about Multi-Level Graph Learning For Audio Event Classification And Human-Perceived Annoyance Rating Prediction
- Log in to post comments
WHO's report on environmental noise estimates that 22 M people suffer from chronic annoyance related to noise caused by audio events (AEs) from various sources. Annoyance may lead to health issues and adverse effects on metabolic and cognitive systems. In cities, monitoring noise levels does not provide insights into noticeable AEs, let alone their relations to annoyance. To create annoyance-related monitoring, this paper proposes a graph-based model to identify AEs in a soundscape, and explore relations between diverse AEs and human-perceived annoyance rating (AR).
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about ECM-OPCC: Efficient Context Model for Octree-based Point Cloud Compression
- Log in to post comments
Recently, deep learning methods have shown promising results in point cloud compression. However, previous octree-based approaches either lack sufficient context or have high decoding complexity (e.g. > 900s). To address this problem, we propose a sufficient yet efficient context model and design an efficient deep learning codec for point clouds. Specifically, we first propose a segment-constrained multi-group coding strategy to exploit the autoregressive context while maintaining decoding efficiency.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about GENEFORMER: LEARNED GENE COMPRESSION USING TRANSFORMER-BASED CONTEXT MODELING
- Log in to post comments
The development of gene sequencing technology sparks an explosive growth of gene data. Thus, the storage of gene data has become an important issue. Recently, researchers begin to investigate deep learning-based gene data compression, which outperforms general traditional methods. In this paper, we propose a transformer-based gene compression method named GeneFormer. Specifically, we first introduce a modified transformer encoder with latent array to eliminate the dependency of the nucleotide sequence.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views