
- Read more about Fast Inverse Mapping of Face GANs
- Log in to post comments
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) synthesize realistic images from random latent vectors. While many studies have explored various training configurations and architectures for GANs, the problem of inverting the generator of GANs has been inadequately investigated. We train a ResNet architecture to map given faces to latent vectors that can be used to generate faces nearly identical to the target. We use a perceptual loss to embed face details in the recovered latent vector while maintaining visual quality using a pixel loss.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views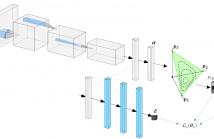
- Read more about Failure Prediction by Confidence Estimation of Uncertainty-Aware Dirichlet Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views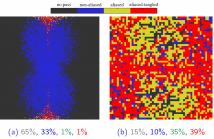

- Read more about Graph Based Transforms based on Graph Neural Networks for Predictive Transform Coding
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces the GBT-NN, a novel class of Graph-based Transform within thecontext of block-based predictive transform coding using intra-prediction. The GBT-NNis constructed by learning a mapping function to map a graph Laplacian representing thecovariance matrix of the current block. Our objective of learning such a mapping functionis to design a GBT that performs as well as the KLT without requiring to explicitly com-pute the covariance matrix for each residual block to be transformed.
- Categories:
 131 Views
131 Views
- Read more about Deep Scattering Network with Max-Pooling
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about DOES SUPER-RESOLUTION IMPROVE OCR PERFORMANCE IN THE REAL WORLD? A CASE STUDY ON IMAGES OF RECEIPTS
- Log in to post comments
Recently, many deep learning methods have been used to handle single image super-resolution (SISR) tasks and often achieve state-of-the-art performance. From a visual point of view, the results look convincing. Yet, does it mean that those techniques are reliable and robust enough to be implemented in real business cases to enhance the performance of other computer vision tasks?
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views
- Read more about Improving Detection and Recognition of Degraded Faces by Discriminative Feature Restoration Using GAN
- Log in to post comments
Face detection and recognition in the wild is currently one of the most interesting and challenging problems. Many algorithms with high performance have already been proposed and applied in real-world applications. However, the problem of detecting and recognising degraded faces from low-quality images and videos mostly remains unsolved. In this paper, we present an algorithm capable of recovering facial features from low-quality videos and images. The resulting output image boosts the performance of existing face detection and recognition algorithms.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly: Neural Networks Straight from JPEG
- Log in to post comments
Over the past decade, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance in many computer vision tasks. They can learn robust representations of image data by processing RGB pixels. Since image data are often stored in a compressed format, from which JPEG is the most widespread, a preliminary decoding process is demanded. Recently, the design of CNNs for processing JPEG compressed data has gained attention from the research community.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about Development of New Fractal and Non-fractal Deep Residual Networks for Deblocking of JPEG Decompressed Images
- Log in to post comments
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Pairwise Adjacency Matrix on Spatial Temporal Graph Convolution Network for Skeleton-based Two-Person Interaction Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Spatial-temporal graph convolutional networks (ST-GCN) have achieved outstanding performances on human action recognition, however, it might be less superior on a two-person interaction recognition (TPIR) task due to the relationship of each skeleton is not considered. In this study, we present an improvement of the ST-GCN model that focused on TPIR by employing the pairwise adjacency matrix to capture the relationship of person-person skeletons (ST-GCN-PAM). To validate the effectiveness of the proposed ST-GCN-PAM model on TPIR, experiments were conducted on NTU RGB+D 120.
- Categories:
 112 Views
112 Views