
- Read more about Fast and High-Quality Singing Voice Synthesis System based on Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
The present paper describes singing voice synthesis based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Singing voice synthesis systems based on deep neural networks (DNNs) are currently being proposed and are improving the naturalness of synthesized singing voices. As singing voices represent a rich form of expression, a powerful technique to model them accurately is required. In the proposed technique, long-term dependencies of singing voices are modeled by CNNs.
- Categories:
 120 Views
120 Views
- Read more about DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS BASED AUTOMATIC SPEECH RECOGNITION FOR FOUR ETHIOPIAN LANGUAGES
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we present speech recognition systems for four Ethiopian languages: Amharic, Tigrigna, Oromo and Wolaytta. We have used comparable training corpora of about 20 to 29 hours speech and evaluation speech of about 1 hour for each of the languages. For Amharic and Tigrigna, lexical and language models of different vocabulary size have been developed. For Oromo and Wolaytta, the training lexicons have been used for decoding.
- Categories:
 153 Views
153 Views
- Read more about Expression Guided EEG Representation Learning for Emotion Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Learning a joint and coordinated representation between different modalities can improve multimodal emotion recognition. In this paper, we propose a deep representation learning approach for emotion recognition from electroencephalogram (EEG) signals guided by facial electromyogram (EMG) and electrooculogram (EOG) signals. We recorded EEG, EMG and EOG signals from 60 participants who watched 40 short videos and self-reported their emotions.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about A NOVEL RANK SELECTION SCHEME IN TENSOR RING DECOMPOSITION BASED ON REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Tensor decomposition has been proved to be effective for solving many problems in signal processing and machine learning. Recently, tensor decomposition finds its advantage for compressing deep neural networks. In many applications of deep neural networks, it is critical to reduce the number of parameters and computation workload to accelerate inference speed in deployment of the network. Modern deep neural network consists of multiple layers with multi-array weights where tensor decomposition is a natural way to perform compression.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views
- Read more about DEEP LEARNING FOR ROBUST POWER CONTROL FOR WIRELESS NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about TEMPORAL CODING IN SPIKING NEURAL NETWORKS WITH ALPHA SYNAPTIC FUNCTION
- Log in to post comments
We propose a spiking neural network model that encodes information in the relative timing of individual neuron spikes and performs classification using the first output neuron to spike. This temporal coding scheme allows the supervised training of the network with backpropagation, using locally exact derivatives of the postsynaptic with respect to presynaptic spike times. The network uses a biologically-inspired alpha synaptic transfer function and trainable synchronisation pulses as temporal references. We successfully train the network on the MNIST dataset encoded in time.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about TEMPORAL CODING IN SPIKING NEURAL NETWORKS WITH ALPHA SYNAPTIC FUNCTION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about An ensemble Based Approach for Generalized Detection of Spoofing Attacks to Automatic Speaker Recognizers
- Log in to post comments
As automatic speaker recognizer systems become mainstream, voice spoofing attacks are on the rise. Common attack strategies include replay, the use of text-to-speech synthesis, and voice conversion systems. While previously-proposed end-to-end detection frameworks have shown to be effective in spotting attacks for one particular spoofing strategy, they have relied on different models, architectures, and speech representations, depending on the spoofing strategy.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views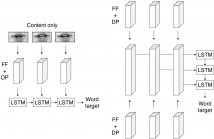
We present a novel lipreading system that improves on the task of speaker-independent word recognition by decoupling motion and content dynamics. We achieve this by implementing a deep learning architecture that uses two distinct pipelines to process motion and content and subsequently merges them, implementing an end-to-end trainable system that performs fusion of independently learned representations. We obtain a average relative word accuracy improvement of ≈6.8% on unseen speakers and of ≈3.3% on known speakers, with respect to a baseline which uses a standard architecture.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
Motivated by the ever-increasing demands for limited communication bandwidth and low-power consumption, we propose a new methodology, named joint Variational Autoencoders with Bernoulli mixture models (VAB), for performing clustering in the compressed data domain. The idea is to reduce the data dimension by Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and group data representations by Bernoulli mixture models (BMMs).
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views