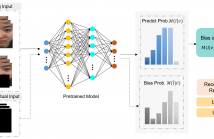
- Read more about CAUSALLY UNCOVERING BIAS IN VIDEO MICRO-EXPRESSION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Detecting microexpressions presents formidable challenges, primarily due to their fleeting nature and the limited diversity in existing datasets. Our studies find that these datasets exhibit a pronounced bias towards specific ethnicities and suffer from significant imbalances in terms of both class and gender representation among the samples. These disparities create fertile ground for various biases to permeate deep learning models, leading to skewed results and inadequate portrayal of specific demographic groups.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Noisy-ArcMix: Additive Noisy Angular Margin Loss Combined With Mixup for Anomalous Sound Detection
- Log in to post comments
Unsupervised anomalous sound detection (ASD) aims to identify anomalous sounds by learning the features of normal operational sounds and sensing their deviations. Recent approaches have focused on the self-supervised task utilizing the classification of normal data, and advanced models have shown that securing representation space for anomalous data is important through representation learning yielding compact intra-class and well-separated intra-class distributions.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views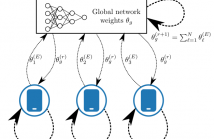
- Read more about Federated Dataset Dictionary Learning For Multi-Source Domain Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
In this article, we propose an approach for federated domain adaptation, a setting where distributional shift exists among clients and some have unlabeled data. The proposed framework, FedDaDiL, tackles the resulting challenge through dictionary learning of empirical distributions. In our setting, clients' distributions represent particular domains, and FedDaDiL collectively trains a federated dictionary of empirical distributions. In particular, we build upon the Dataset Dictionary Learning framework by designing collaborative communication protocols and aggregation operations.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views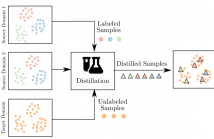
- Read more about Multi-Source Domain Adaptation meets Dataset Distillation through Dataset Dictionary Learning
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we consider the intersection of two problems in machine learning: Multi-Source Domain Adaptation (MSDA) and Dataset Distillation (DD). On the one hand, the first considers adapting multiple heterogeneous labeled source domains to an unlabeled target domain. On the other hand, the second attacks the problem of synthesizing a small summary containing all the information about the datasets. We thus consider a new problem called MSDA-DD.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
Weak-label learning is a challenging task that requires learning from data "bags" containing positive and negative instances, but only the bag labels are known. The pool of negative instances is usually larger than positive instances, thus making selecting the most informative negative instance critical for performance. Such a selection strategy for negative instances from each bag is an open problem that has not been well studied for weak-label learning.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views
Contrastive learning has demonstrated great effectiveness in representation learning especially for image classification tasks. However, there is still a shortage in the studies targeting regression tasks, and more specifically applications on hyperspectral data. In this paper, we propose a contrastive learning framework for the regression tasks for hyperspectral data. To this end, we provide a collection of transformations relevant for augmenting hyperspectral data, and investigate contrastive learning for regression.
ICASSP_PPT.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Poster for the paper "Revisiting Deep Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis"
- Log in to post comments
Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is a classic statistical method for discovering latent co-variation that underpins two or more observed random vectors. Several extensions and variations of CCA have been proposed that have strengthened our capabilities in terms of revealing common random factors from multiview datasets. In this work, we first revisit the most recent deterministic extensions of deep CCA and highlight the strengths and limitations of these state-of-the-art methods. Some methods allow trivial solutions, while others can miss weak common factors.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views- Read more about TOWARDS FASTER END-TO-END DATA TRANSMISSION OVER VOICE CHANNELS
- Log in to post comments
As new technologies spread, phone fraud crimes have become master strategies to steal money and personal identities. Inspired by website authentication, we propose an end-to-end data modem over voice channels that can transmit the caller’s digital certificate to the callee for verification. Without assistance from telephony providers, it is difficult to carry useful information over voice channels. For example, voice activity detection may quickly classify the encoded signals as nonspeech signals and reject the input waveform.
会议海报-终稿.pdf
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about HIERARCHICAL VAE BASED SEMANTIC COMMUNICATIONS FOR POMDP TASKS
- Log in to post comments
Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) is a general framework for a wide range of control tasks, which can benefit from enabling semantic communicatons among different agents. Semantic communications aim to exchange compact messages that can convey task-relevant information between agents. A critical problem in semantic communication is source representation learning, which is governed by a fundamental tradeoff between compactness and sufficiency. Such a tradeoff is still underinvestigated in the context of POMDP.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Improving Cross-domain Few-shot Classification with Multilayer Perceptron
- Log in to post comments
Cross-domain few-shot classification (CDFSC) is a challenging and tough task due to the significant distribution discrepancies across different domains. To address this challenge, many approaches aim to learn transferable representations. Multilayer perceptron (MLP) has shown its capability to learn transferable representations in various downstream tasks, such as unsupervised image classification and supervised concept generalization. However, its potential in the few-shot settings has yet to be comprehensively explored.
- Categories:
 143 Views
143 Views