
- Read more about ADVERSARIAL EXAMPLE DETECTION BAYESIAN GAME
- Log in to post comments
Despite the increasing attack ability and transferability of adversarial examples (AE), their security, i.e., how unlikely they can be detected, has been ignored more or less. Without the ability to circumvent popular detectors, the chance that an AE successfully fools a deep neural network is slim. This paper gives a game theory analysis of the interplay between an AE attacker and an AE detection investigator. Taking the perspective of a third party, we introduce a game theory model to evaluate the ultimate performance when both the attacker and the investigator are aware of each other.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Image Reconstruction Without Explicit Priors
- Log in to post comments
We consider solving ill-posed imaging inverse problems without access to an explicit image prior or ground-truth examples. An overarching challenge in inverse problems is that there are many undesired images that fit to the observed measurements, thus requiring image priors to constrain the space of possible solutions to more plausible reconstructions. However, in many applications it is difficult or potentially impossible to obtain ground-truth images to learn an image prior. Thus, inaccurate priors are often used, which inevitably result in biased solutions.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Transductive Matrix Completion with Calibration for Multi-Task Learning
- Log in to post comments
Multi-task learning has attracted much attention due to growing multi-purpose research with multiple related data sources. Moreover, transduction with matrix completion is a useful method in multi-label learning. In this paper, we propose a transductive matrix completion algorithm that incorporates a calibration constraint for the features under the multi-task learning framework. The proposed algorithm recovers the incomplete feature matrix and target matrix simultaneously. Fortunately, the calibration information improves the completion results.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Rain Estimation Over a Region Using CycleGan
- Log in to post comments
In the last couple of years, supervised machine learning (ML) methods have shown state-of-the-art results for near-ground rain estimation. Information is usually obtained from two kinds of sensors - rain gauges, which measure rain rate, and commercial microwave links (CMLs) which measure attenuation. These data sources are paired to create a dataset on which a model is trained.
The arising problem of such methods of training is in the need for the datasets to be constructed with a CML-rain gauge pairing relation.
- Categories:
 91 Views
91 Views- Read more about Calibrating AI Models for Few-Shot Demodulation via Conformal Prediction
- Log in to post comments
Artificial Intelligent (AI) tools can be useful to address model deficits in the design of communication systems. However, conventional learning-based AI algorithms yield poorly calibrated decisions, unabling to quantify their outputs uncertainty. While Bayesian learning can enhance calibration by capturing epistemic uncertainty caused by limited data availability, formal calibration guarantees only hold under strong assumptions about the ground-truth, unknown, data generation mechanism.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views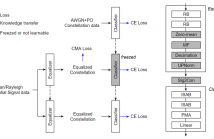
- Read more about EMC²-Net: Joint Equalization and Modulation Classification Based on Constellation Network
- Log in to post comments
Modulation classification (MC) is the first step performed at the receiver side unless the modulation type is explicitly indicated by the transmitter. Machine learning techniques have been widely used for MC recently. In this paper, we propose a novel MC technique dubbed as Joint Equalization and Modulation Classification based on Constellation Network (EMC²-Net). Unlike prior works that considered the constellation points as an image, the proposed EMC²-Net directly uses a set of 2D constellation points to perform MC.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views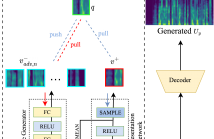
- Read more about CNEG-VC: Contrastive Learning using Hard Negative Example in Non-parallel Voice Conversion
- Log in to post comments
Contrastive learning has advantages for non-parallel voice conversion, but the previous conversion results could be better and more preserved. In previous techniques, negative samples were randomly selected in the features vector from different locations. A positive example could not be effectively pushed toward the query examples. We present contrastive learning in non-parallel voice conversion to solve this problem using hard negative examples. We named it CNEG-VC. Specifically, we teach the generator to generate negative examples. Our proposed generator has specific features.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Grassmannian Dimensionality Reduction Using Triplet Margin Loss for UME Classification of 3D Point Clouds
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about NVC-Net: End-to-End Adversarial Voice Conversion
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views