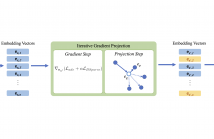
- Read more about BLOCK-SPARSE ADVERSARIAL ATTACK TO FOOL TRANSFORMER-BASED TEXT CLASSIFIERS
- Log in to post comments
Recently, it has been shown that, in spite of the significant performance of deep neural networks in different fields, those are vulnerable to adversarial examples. In this paper, we propose a gradient-based adversarial attack against transformer-based text classifiers. The adversarial perturbation in our method is imposed to be block-sparse so that the resultant adversarial example differs from the original sentence in only a few words. Due to the discrete nature of textual data, we perform gradient projection to find the minimizer of our proposed optimization problem.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views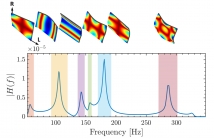
- Read more about On the Prediction of the Frequency Response of a Wooden Plate from its Mechanical Parameters
- Log in to post comments
Inspired by deep learning applications in structural mechanics, we focus on how to train two predictors to model the relation between the vibrational response of a prescribed point of a wooden plate and its material properties. In particular, the eigenfrequencies of the plate are estimated via multilinear regression, whereas their amplitude is predicted by a feedforward neural network.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views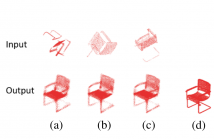
- Read more about CF-NET: COMPLEMENTARY FUSION NETWORK FOR ROTATION INVARIANT POINT CLOUD COMPLETION
- Log in to post comments
Real-world point clouds usually have inconsistent orientations and often suffer from data missing issues. To solve this problem, we design a neural network, CF-Net, to address challenges in rotation invariant completion. In our network, we modify and integrate complementary operators to extract features that are robust against rotation and incompleteness. Our CF-Net can achieve competitive results both geometrically and semantically as demonstrated in this paper.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Dynimp: Dynamic Imputation for Wearable Sensing Data through Sensory and Temporal Relatedness
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Dynimp: Dynamic Imputation for Wearable Sensing Data through Sensory and Temporal Relatedness
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Fast learning of fast transforms, with guarantees (ICASSP 2022 poster)
- Log in to post comments
Approximating a matrix by a product of few sparse factors whose supports possess the butterfly structure, which is common to many fast transforms, is key to learn fast transforms and speed up algorithms for inverse problems. We introduce a hierarchical approach that recursively factorizes the considered matrix into two factors. Using recent advances on the well-posedness and tractability of the two-factor fixed-support sparse matrix factorization problem, the proposed algorithm is endowed with exact recovery guarantees.
poster_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Category-Adaptive Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about END-TO-END NETWORK BASED ON TRANSFORMER FOR AUTOMATIC DETECTION OF COVID-19
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about ADAPTIVE WIRELESS POWER ALLOCATION WITH GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views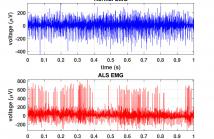
- Read more about ALSNET: A DILATED 1-D CNN FOR IDENTIFYING ALS FROM RAW EMG SIGNAL (Presentation Slides)
- Log in to post comments
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is one of the most common neuromuscular diseases which affects both lower and upper motor neurons. In this paper, a dilated one dimensional convolutional neural network, named ALSNet, is proposed for identifying ALS from raw EMG signal. No hand-crafted feature extraction is required, rather, ALSNet is able to take raw EMG signal as input and detect EMG signals of ALS subjects. This makes the method more feasible for practical implementation by reducing the computational cost required for extracting features.
- Categories:
 539 Views
539 Views