- Read more about ALSNET: A DILATED 1-D CNN FOR IDENTIFYING ALS FROM RAW EMG SIGNAL (Poster)
- Log in to post comments
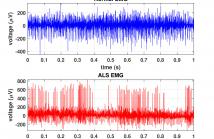
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is one of the most common neuromuscular diseases which affects both lower and upper motor neurons. In this paper, a dilated one dimensional convolutional neural network, named ALSNet, is proposed for identifying ALS from raw EMG signal. No hand-crafted feature extraction is required, rather, ALSNet is able to take raw EMG signal as input and detect EMG signals of ALS subjects. This makes the method more feasible for practical implementation by reducing the computational cost required for extracting features.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Fast learning of fast transforms, with guarantees (ICASSP 2022 video)
- Log in to post comments
Approximating a matrix by a product of few sparse factors whose supports possess the butterfly structure, which is common to many fast transforms, is key to learn fast transforms and speed up algorithms for inverse problems. We introduce a hierarchical approach that recursively factorizes the considered matrix into two factors. Using recent advances on the well-posedness and tractability of the two-factor fixed-support sparse matrix factorization problem, the proposed algorithm is endowed with exact recovery guarantees.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING TRANSFERABILITY MEASURES AND DOMAIN SELECTION IN CROSS-DOMAIN SLOT FILLING
- Log in to post comments
As an essential task for natural language understanding, slot filling aims to identify the contiguous spans of specific slots in an utterance. In real-world applications, the labeling costs of utterances may be expensive, and transfer learning techniques have been developed to ease this problem. However, cross-domain slot filling could significantly suffer from negative transfer due to non-targeted or zero-shot slots.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about ChunkFusion: A Learning-based RGB-D 3D Reconstruction Framework via Chunk-wise Integration
- Log in to post comments
Recent years have witnessed a growing interest in online RGB-D 3D reconstruction. On the premise of ensuring the reconstruction accuracy with noisy depth scans, making the system scalable to various environments is still challenging. In this paper, we devote our efforts to try to fill in this research gap by proposing a scalable and robust RGB-D 3D reconstruction framework, namely ChunkFusion. In ChunkFusion, sparse voxel management is exploited to improve the scalability of online reconstruction.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about REGRESSION ASSISTED MATRIX COMPLETION FOR RECONSTRUCTING A PROPAGATION FIELD WITH APPLICATION TO SOURCE LOCALIZATION
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP2022.pdf
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Iterative Machine-Learning-Based Method of Selecting Encoder Parameters for Speed-Bitrate Tradeoff
- Log in to post comments
Modern codecs offer numerous settings that can nonuniformly alter the encoding process. Some researchers have proposed video encoding multiobjective optimization, but none of these proposals addresses optimization of the entire encoder's option space when it is large. In this paper, we present a method for multiobjective encoding optimization of a given encoder in terms of relative video bitrate and encoding speed. The process takes place over one or more videos against a set of reference presets. It actively exploits similarities in the encoding process for similar videos.
DCC2022-v2.pdf
- Categories:
 228 Views
228 Views
- Read more about A Physics-Informed Vector Quantized Autoencoder for Data Compression of Turbulent Flow
- Log in to post comments
Analyzing large-scale data from simulations of turbulent flows is memory intensive, requiring significant resources. This major challenge highlights the need for data compression techniques. In this study, we apply a physics-informed Deep Learning technique based on vector quantization to generate a discrete, low-dimensional representation of data from simulations of three-dimensional turbulent flows.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about End-to-end lossless compression of high precision depth maps guided by pseudo-residual
- Log in to post comments
DCC_pre.pdf
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Describe me if you can! Characterized instance-level human parsing
- Log in to post comments
Several computer vision applications such as person search or online fashion rely on human description. The use of instance-level human parsing (HP) is therefore relevant since it localizes semantic attributes and body parts within a person. But how to characterize these attributes? To our knowledge, only some single-HP datasets describe attributes with some color, size and/or pattern characteristics. There is a lack of dataset for multi-HP in the wild with such characteristics.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about DEPTH CORRECTION FOR TIME-OF-FLIGHT CAMERA USING DEPTH DISTORTION DEPENDENCY ON PULSE WIDTH OF IRRADIATED LIGHT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views