
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about Structure of the Set of Signals With Strong Divergence of the Shannon Sampling Series
- Log in to post comments
It is known that there exist signals in Paley-Wiener space $PW_\pi^1$ of bandlimited signals with absolutely integrable Fourier transform, for which the peak value of the Shannon sampling series diverges unboundedly. In this paper we analyze the structure of the set of signals which lead to strong divergence. Strong divergence is closely linked to the existence of adaptive methods. We prove that there exists an infinite dimensional closed subspace of $PW_\pi^1$, all signals of which, except the zero signal, lead to strong divergence of the peak value of the Shannon sampling series.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Blind Image Deconvolution Using Student’s-t Prior With Overlapping Group Sparsity
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we solve blind image deconvolution problem that is to remove blurs form a signal degraded image without any knowledge of the blur kernel. Since the problem is ill-posed, an image prior plays a significant role in accurate blind deconvolution. Traditional image prior assumes coefficients in filtered domains are sparse. However, it is assumed here that there exist additional structures over the sparse coefficients. Accordingly, we propose new problem formulation for the blind image deconvolution, which utilize the structural
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about FROM FOCAL STACKS TO TENSOR DISPLAY: A METHOD FOR LIGHT FIELD VISUALIZATION WITHOUT MULTI-VIEW IMAGES
- Log in to post comments
A new type of light field display called a tensor display was investigated. Although this display consists of only a few light attenuating
layers located in front of a backlight, many views can be emitted in different directions simultaneously without sacrificing the resolution
of each view. The transmittance pattern of each layer is calculated from a light field, namely, a set of dense multi-view images (typically
dozens) that are to be observed from different directions. However, preparing such images is often cumbersome for real objects. We propose
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 ViewsMetric learning for music is an important problem for many music information retrieval (MIR) applications such as music generation, analysis, retrieval, classification and recommendation. Traditional music metrics are mostly defined on linear transformations of handcrafted audio features, and may be improper in many situations given the large variety of mu- sic styles and instrumentations.
presentation.pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views- Read more about Polyphonic Piano Note Transcription with Non-negative Matrix Factorization of Differential Spectrogram
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about A Dual Estimation Approach for Removing the Show-Through Effect in the Scanned Documents
- Log in to post comments
The digital scans of double sided documents suffer from distortions because the contents on the back side of the document often shows up on the front side in the scans and vice-versa either due to transparency of the paper or due to ink-bleeding. This is show-through effect. In this paper a state-space based approach is proposed for removing this commonly found contamination in the scans of duplex printed documents. Separate state-space representation for signals and parameters are defined and a dual state-parameter estimation approach is employed to alleviate the degradation in the scans.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Appearance-Based Gesture Recognition in The Compressed Domain - Poster
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel appearance-based gesture recognition algorithm using compressed domain signal processing tech- niques. Gesture features are extracted directly from the compressed measurements, which are the block averages and the coded linear combinations of the image sensor’s pixel values. We also improve both the computational efficiency and the memory requirement of the previous DTW-based K-NN gesture classifiers. Both simulation testing and hardware implementation strongly support the proposed algorithm.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Part-Level Fully Convolutional Networks for Pedestrian Detection
- Log in to post comments
Since pedestrians in videos have a wide range of appearances such as body poses, occlusions, and complex backgrounds, pedestrian detection is a challengeable task. In this paper, we propose part-level fully convolutional networks (FCN) for pedestrian detection. We adopt deep learning to deal with the proposal shifting problem in pedestrian detection. First, we combine convolutional neural networks (CNN) and FCN to align bounding boxes for pedestrians. Then, we perform part-level pedestrian detection based on CNN to recall the lost body parts.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views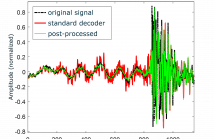
- Read more about Pre-Echo Noise Reduction in Frequency-Domain Audio Codecs (Poster)
- Log in to post comments
One of the most common yet detrimental compression artifacts in frequency-domain audio codecs is known as pre-echo, which is perceived as a brief noise preceding transient signals, and is discernable even without direct comparison to the original signal. Because of its substantial negative impact on audio quality, many techniques have been proposed to alleviate it, but not without effect on coding efficiency.
jim-poster.pdf
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views- Read more about A Robust FISTA-Like Algorithm
- Log in to post comments
The Fast Iterative Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm (FISTA) is regarded as the state-of-the-art among a number of proximal gradient-based methods used for addressing large-scale optimization problems with simple but non-differentiable objective functions. However, the efficiency of FISTA in a wide range of applications is hampered by a simple drawback in the line search scheme. The local estimate of the Lipschitz constant, the inverse of which gives the step size, can only increase while the algorithm is running.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views