
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about An Iterative Time Domain Denoising Method
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on the classical additive noise signal restoration problem. The proposed time domain denoising method iteratively removes outliers. The proposed denoising filter incorporates a threshold operation to determine which sample values are outliers. This method is compared with wavelet soft/hard thresholding and empirical mode decomposition interval thresholding. The proposed method is shown to be a promising method to denoise signals where a frequency decomposition may not be a robust representation of the noise free signal.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Improve Diverse Text Generation by Self Labeling Conditional Variational Auto Encoder
- Log in to post comments
Diversity plays a vital role in many text generating applications. In recent years, Conditional Variational Auto Encoders (CVAE) have shown promising performances for this task. However, they often encounter the so called KL-Vanishing problem. Previous works mitigated such problem by heuristic methods such as strengthening the encoder or weakening the decoder while optimizing the CVAE objective function. Nevertheless, the optimizing direction of these methods are implicit and it is hard to find an appropriate degree to which these methods should be applied.
slcvae.pptx
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views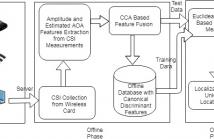
- Read more about FuseLoc: A CCA Based Information Fusion for Indoor Localization Using CSI Phase and Amplitude of WiFi Signals
- Log in to post comments
With the growth of location based services, indoor localization is attracting great interests as it facilitates further ubiquitous environments. In this paper, we propose FuseLoc, the first information fusion based indoor localization using multiple features extracted from Channel State Information (CSI). In FuseLoc, the localization problem is modelled as a pattern matching problem, where the location of a subject is predicted based on the similarity measure of the CSI features of the unknown location with those of the training locations.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Methodical Design and Trimming of Deep Learning Networks: Enhancing External BP learning with Internal Omnipresent-Supervision Training Paradigm
- Log in to post comments
Back-propagation (BP) is now a classic learning paradigm
whose source of supervision is exclusively from the external
(input/output) nodes. Consequently, BP is easily vulnerable
to curse-of-depth in (very) Deep Learning Networks
(DLNs). This prompts us to advocate Internal Neuron’s
Learnablility (INL) with (1)internal teacher labels (ITL); and
(2)internal optimization metrics (IOM) for evaluating hidden
layers/nodes. Conceptually, INL is a step beyond the notion
of Internal Neuron’s Explainablility (INE), championed by
ICASSP2019.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about A New Spatial Steganographic Scheme by Modeling Image Residuals with Multivariate Gaussian Model
- Log in to post comments
Embedding costs used in content-adaptive image steganographic schemes can be defined in a heuristic way or with a statistical model. Inspired by previous steganographic methods, i.e., MG (multivariate Gaussian model) and MiPOD (minimizing the power of optimal detector), we propose a model-driven scheme in this paper. Firstly, we model image residuals obtained by high-pass filtering with quantized multivariate Gaussian distribution. Then, we derive the approximated Fisher Information (FI). We show that FI is related to both Gaussian variance and filter coefficients.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
Community detection from graphs has many applications
in machine learning, biological and social sciences. While
there is a broad spectrum of literature based on various
approaches, recently there has been a significant focus on
inference algorithms for statistical models of community
structure. These algorithms strive to solve an inference
problem based on a generative model of the network. Recent
advances in stochastic gradient MCMC have played a crucial
role in improving the scalability of these techniques. In this
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about HAND GRAPH REPRESENTATIONS FOR UNSUPERVISED SEGMENTATION OF COMPLEX ACTIVITIES
- Log in to post comments
Analysis of hand skeleton data can be used to understand patterns in manipulation and assembly tasks. This paper introduces a graphbased representation of hand skeleton data and proposes a method to perform unsupervised temporal segmentation of a sequence of subtasks in order to evaluate the efficiency of an assembly task. We explore the properties of different choices of hand graphs and their spectral decomposition. A comparative performance of these graphs is presented in the context of complex activity segmentation.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Frequency-selective hybrid precoding and combining for mmWave MIMO systems with per-antenna power constraints
- Log in to post comments
Configuring hybrid precoders and combiners is the main challenge to be solved to operate at millimeter wave (mmWave) frequencies. The use of hybrid architectures imposse hardware constraints on the analog precoder that need to be carefully dealt with. In this paper, we develop hybrid precoders and combiners aiming at minimizing the Euclidean distance with respect to the approximate all-digital precoders and combiners maximizing the spectral efficiency under per-antenna power constraints.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views