
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about Graph Spectral Domain Blind Watermarking
- Log in to post comments
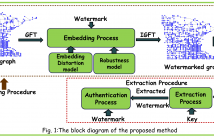
This paper proposes the first ever graph spectral domain blind watermarking algorithm. We explore the recently developed graph signal processing for spread-spectrum watermarking to authenticate the data recorded on non-Cartesian grids, such as sensor data, 3D point clouds, Lidar scans and mesh data. The choice of coefficients for embedding the watermark is driven by the model for minimisation embedding distortion and the robustness model.
- Categories:
 67 Views
67 Views
- Read more about Improving Children Speech Recognition through Feature Learning from Raw Speech Signal
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Second order sequential best rotation algorithm with Householder reduction for polynomial matrix eigenvalue decomposition
- Log in to post comments
The Second-order Sequential Best Rotation (SBR2) algorithm, used for Eigenvalue Decomposition (EVD) on para-Hermitian polynomial matrices typically encountered in wideband signal processing applications like multichannel Wiener filtering and channel coding, involves a series of delay and rotation operations to achieve diagonalisation. In this paper, we proposed the use of Householder transformations to reduce polynomial matrices to tridiagonal form before zeroing the dominant element with rotation.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Learning Voice Source Related Information for Depression Detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views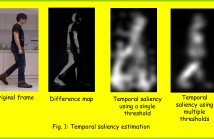
- Read more about Temporal Salience Based Human Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a new approach for human action recognition exploring the temporal salience. We exploit features over the temporal saliency maps for learning the action representation using a local dense descriptor. This approach automatically guides the descriptor towards the most interesting contents, i.e. the salience region, and obtains the action representation using solely the saliency information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about COMMON MODE PATTERNS FOR SUPERVISED TENSOR SUBSPACE LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Segment-level training based on Confidence Measures for Hybrid HMM/ANN Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about UNMIXING DYNAMIC PET IMAGES: COMBINING SPATIAL HETEROGENEITY AND NON-GAUSSIAN NOISE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Updates In Bayesian Filtering By Continuous Projections On A Manifold Of Densities
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we develop a novel method for approximate continuous-discrete Bayesian filtering. The projection filtering framework is exploited to develop accurate approximations of posterior distributions within parametric classes of probability distributions. This is done by formulating an ordinary differential equation for the posterior distribution that has the prior as initial value and hits the exact posterior after a unit of
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about A Fast Method of Computing Persistent Homology of Time Series Data
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views