
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Modeling nonlinear audio effects with end-to-end deep neural networks
- Log in to post comments
Audio processors whose parameters are modified periodically
over time are often referred as time-varying or modulation based
audio effects. Most existing methods for modeling these type of
effect units are often optimized to a very specific circuit and cannot
be efficiently generalized to other time-varying effects. Based on
convolutional and recurrent neural networks, we propose a deep
learning architecture for generic black-box modeling of audio processors
with long-term memory. We explore the capabilities of
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about An End-to-End Network to Synthesize Intonation using a Generalized Command Response Model - Poster
- Log in to post comments
The generalized command response (GCR) model represents intonation as a
superposition of muscle responses to spike command signals. We have previously
shown that the spikes can be predicted by a two-stage system, consisting of a recurrent neural network and a post-processing procedure, but the responses themselves were fixed dictionary atoms. We propose an end-to-end
neural architecture that replaces the dictionary atoms with trainable
second-order recurrent elements analogous to recursive filters. We demonstrate
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Views
- Read more about Towards learned color representations for image splicing detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Towards learned color representations for image splicing detection
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Deep CNN for Wideband mmWave Massive MIMO Channel Estimation using Frequency Correlation
- Log in to post comments
For millimeter wave (mmWave) systems with large-scale arrays, hybrid processing structure is usually used at both transmitters and receivers to reduce the complexity and cost, which poses a very challenging issue in channel estimation, especially at the low transmit signal-to-noise ratio regime. In this paper, deep convolutional neural network (CNN) is employed to perform wideband channel estimation for mmWave massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views
- Read more about 1-D Convolutional Neural Networks for Signal Processing Applications
- Log in to post comments
1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have recently become the state-of-the-art technique for crucial signal processing applications such as patient-specific ECG classification, structural health monitoring, anomaly detection in power electronics circuitry and motor-fault detection. This is an expected outcome as there are numerous advantages of using an adaptive and compact 1D CNN instead of a conventional (2D) deep counterparts.
- Categories:
 420 Views
420 Views
3D shape recognition has attracted a great interest in computer vision due to its large number of important and exciting applications. This has led to exploring a variety of approaches to develop more efficient 3D analysis methods. However, current works take into account descriptions of global shape to generate models, ignoring small differences causing the problem of mismatching, especially for high similarity shapes.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views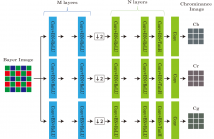
- Read more about IMAGE DEMOSAICKING VIA CHROMINANCE IMAGES WITH PARALLEL CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Many conventional demosaicking methods are based on hand-crafted filters. However, the filters yield false colors in salient regions like edges and textures. For acquisition of high quality images, we focus on neural networks. Neural networks lead to high accuracy in many fields. However, there are few methods in demosaicking field. For adaptation to demosaicking, we consider not only network's architecture but also the input. In this research, we utilize a Bayer image as input of our networks.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Clonability of anti-counterfeiting printable graphical codes: a machine learning approach
- Log in to post comments
2019_ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views