
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Proximal Deep Recurrent Neural Network for Monaural Singing Voice Separation
- Log in to post comments
The recent deep learning methods can offer state-of-the-art performance for Monaural Singing Voice Separation (MSVS). In these deep methods, the recurrent neural network (RNN) is widely employed. This work proposes a novel type of Deep RNN (DRNN), namely Proximal DRNN (P-DRNN) for MSVS, which improves the conventional Stacked RNN (S-RNN) by introducing a novel interlayer structure. The interlayer structure is derived from an optimization problem for Monaural Source Separation (MSS).
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A DEEP NEURAL NETWORK BASED END TO END MODEL FOR JOINT HEIGHT AND AGE ESTIMATION FROM SHORT DURATION SPEECH
- Log in to post comments
Automatic height and age prediction of a speaker has a wide variety of applications in speaker profiling, forensics etc. Often in such applications only a few seconds of speech data is available to reliably estimate the speaker parameters. Traditionally, age and height were predicted separately using different estimation algorithms. In this work, we propose a unified DNN architecture to predict both height and age of a speaker for short durations of speech.
- Categories:
 55 Views
55 Views
- Read more about Proximal Deep Recurrent Neural Network for Monaural Singing Voice Separation
- Log in to post comments
The recent deep learning methods can offer state-of-the-art performance for Monaural Singing Voice Separation (MSVS). In these deep methods, the recurrent neural network (RNN) is widely employed. This work proposes a novel type of Deep RNN (DRNN), namely Proximal DRNN (P-DRNN) for MSVS, which improves the conventional Stacked RNN (S-RNN) by introducing a novel interlayer structure. The interlayer structure is derived from an optimization problem for Monaural Source Separation (MSS).
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Sensing Matrix Design for Greedy Algorithms in MMV Compressive Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Sensing matrix can be designed with low coherence with the measurement matrix to improve the sparse signal recovery performance of greedy algorithms. However, most of the sensing matrix design algorithms are computationally expensive due to large number of iterations. This paper proposes an iteration-free sensing matrix design algorithm for multiple measurement vectors (MMV) compressive sensing.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about FINE-TUNING APPROACH TO NIR FACE RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Despite extensive researches for face recognition (FR), it is still difficult to apply deep CNN models to NIR FR due to a lack of training data. In this study, we propose a fine-tuning approach to allow deep CNN models to be applied to NIR FR with small training datasets. In the proposed approach, parameters of deep CNN models for RGB FR are utilized as initial parameters to train deep CNN models for NIR FR. The proposed approach has two main advantages: 1) High NIR FR performances can be achieved with very small public training datasets.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about GPU-BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF BELIEF PROPAGATION DECODING FOR POLAR CODES
- Log in to post comments
Belief Propagation (BP) decoding provides soft outputs and features high-level parallelism. In this paper, we propose an optimized software BP decoder for polar codes on graphics processing units (GPUs). A full-parallel decoding architecture for codes with length n ≤ 2048 is presented to simultaneously update n/2 processing elements (PEs) within each stage and achieve high on-chip memory utilization by using
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views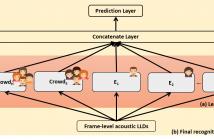
- Read more about EVERY RATING MATTERS: JOINT LEARNING OF SUBJECTIVE LABELS AND INDIVIDUAL ANNOTATORS FOR SPEECH EMOTION CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
The subjectivity and variability exist in the human emotion perception differs from person to person. In this work, we propose a framework that models the majority of emotion annotation integrated with modeling of subjectivity in improving emotion categorization performances. Our method achieves a promising accuracy of 61.48% on a four-class emotion recognition task. To the best of our knowledge, while there are many works in studying annotator subjectivity, this is one of the first works that have explicitly modeled jointly the consensus with individuality in emotion perception to demonstrate its improvement in classifying emotion in a benchmark corpus.
In our immediate future work, we will evaluate the proposed framework on other public large-scaled emotional database with multiple annotators, e.g., NNIME, to further justify its robustness. We also plan to extend our framework to includ other behavior attributes, e.g., lexical content and body movements. Furthermore, the subjective nature of emotion perception has been shown to be related to the rater personality, a joint modeling of rater’s characteristics with his/her subjectivity in emotion perception may lead to further advancement in robust emotion recognition.
- Categories:
 83 Views
83 Views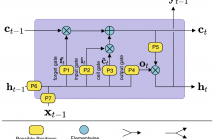
- Read more about Gaussian Process LSTM Recurrent Neural Network Language Models for Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Recurrent neural network language models (RNNLMs) have shown superior performance across a range of speech recognition tasks. At the heart of all RNNLMs, the activation functions play a vital role to control the information flows and tracking longer history contexts that are useful for predicting the following words. Long short-term memory (LSTM) units are well known for such ability and thus widely used in current RNNLMs. However, the deterministic parameter estimates in LSTM RNNLMs are prone to over-fitting and poor generalization when given limited training data.
- Categories:
 122 Views
122 Views