
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Fast Implementation of Double-coupled Nonnegative Canonical Polyadic Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Real-world data exhibiting high order/dimensionality and various couplings are linked to each other since they share
some common characteristics. Coupled tensor decomposition has become a popular technique for group analysis in recent
years, especially for simultaneous analysis of multi-block tensor data with common information. To address the multi-
block tensor data, we propose a fast double-coupled nonnegative Canonical Polyadic Decomposition (FDC-NCPD)
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about AN IMPROVED AIR TISSUE BOUNDARY SEGMENTATION TECHNIQUE FOR REAL TIME MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING VIDEO USING SEGNET
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an improved methodology for the segmentation of the Air-Tissue boundaries (ATBs) in the upper airway of the human vocal tract using Real-Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging (rtMRI) videos. Semantic segmentation is deployed in the proposed approach using a Deep learning architecture called SegNet. The network processes an input image to produce a binary output image of the same dimensions having classified each pixel as air cavity or tissue, following which contours are predicted. A Multi-dimensional least square smoothing technique is applied to smoothen the contours.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views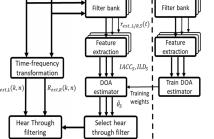
- Read more about PARAMETRIC HEAR THROUGH EQUALIZATION FOR AUGMENTED REALITY AUDIO
- Log in to post comments
Augmented Reality (AR) audio applications require headphones to be acoustically transparent so that real sounds can pass through unaltered for natural fusion with virtual sounds. In this paper, we consider a multiple source scenario for hear through (HT) equalization (EQ) using closed-back circumaural headsets. AR headset prototype (described in our previous study) is used to capture real sounds from external microphones and compute the directional HT filters using adaptive filtering.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views
- Read more about Hierarchy-aware Loss Function on a Tree Structured Label Space for Audio Event Detection
- Log in to post comments
The paper introduces a hierarchy-aware loss function in a Deep Neural Network for an audio event detection task that has a bi-level tree structured label space. The goal is not only to improve audio event detection performance at all levels in the label hierarchy, but also to produce better audio embeddings. We exploit the label tree structure to preserve that information in the hierarchy-aware loss function. Two different loss functions are separately employed. First, a triplet loss with probabilistic multi-level batch mining is introduced.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views
- Read more about Interference Exploitation Precoding for Multi-Level Modulations
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the interference exploitation precoding for multi-level modulations in the downlink multi-antenna systems. We mathematically derive the optimal precoding structures based on the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions. Furthermore, by formulating the dual problem, the precoding problem for multi-level modulations can be transformed into a pre-scaling operation using quadratic programming (QP) optimization.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about AIR-TISSUE BOUNDARY SEGMENTATION IN REAL TIME MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING VIDEO USING A CONVOLUTIONAL ENCODER-DECODER NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a convolutional encoder-decoder network (CEDN) based approach for upper and lower Air-Tissue Boundary (ATB) segmentation within vocal tract in real-time magnetic resonance imaging (rtMRI) video frames. The output images from CEDN are processed using perimeter and moving average filters to generate smooth contours representing ATBs. Experiments are performed in both seen subject and unseen subject conditions to examine the generalizability of the CEDN based approach.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about AN LS LOCALISATION METHOD FOR MASSIVE MIMO TRANSMISSION SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel localization method based on directional beams,
as available in novel massive MIMO transmission techniques instead
of radius information, and derive a least squares (LS) estimation
method. The new method is a direct LS method that can be solved by
a linear set of equations rather than an iterative method required for
radius information. In a further step, we also show how to transform
radius information into virtual beams to apply the proposed method.
Finally, we evaluate the accuracy of the new methods by simulations.
poster_v2.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about FORMANT-GAPS FEATURES FOR SPEAKER VERIFICATION USING WHISPERED SPEECH
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we propose a new feature based on formants for whispered speaker verification (SV) task, where neutral data is used for enrollment and whispered recordings are used for test. Such a mismatch between enrollment and test often degrades the performance of whispered SV systems due to the difference in acoustic characteristics of whispered and neutral speech. We hypothesize that the proposed formant and formant gap (F oG) features are more invariant to the modes of speech in capturing speaker specific information
wsv_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Asymptotic Performance of Linear Discriminant Analysis with Random Projections
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views