
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about CLEANING ADVERSARIAL PERTURBATIONS VIA RESIDUAL GENERATIVE NETWORK FOR FACE VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have recently achieved impressive performances on various applications. However, recent researches show that DNNs are vulnerable to adversarial perturbations injected into input samples. In this paper, we investigate a defense method for face verification: a deep residual generative network (ResGN) is learned to clean adversarial perturbations. We propose a novel training framework composed of ResGN, pre-trained VGG-Face network and FaceNet network.
poster苏玉莹.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views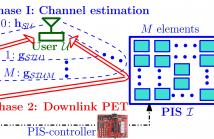
- Read more about Channel Estimation and Low-complexity Beamforming Design for Passive Intelligent Surface Assisted MISO Wireless Energy Transfer
- Log in to post comments
Usage of passive intelligent surface (PIS) is emerging as a low-cost green alternative to massive antenna systems for realizing high energy beamforming (EB) gains. To maximize its realistic utility, we present a novel channel estimation (CE) protocol for PIS-assisted energy transfer (PET) from a multiantenna power beacon (PB) to a single-antenna energy harvesting (EH) user. Noting the practical limitations of PIS and EH user, all computations are carried out at PB having required active components and radio resources.
- Categories:
 134 Views
134 Views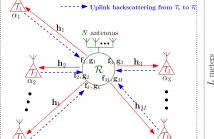
- Read more about Sum Throughput Maximization For Multi-Tag MISO Backscattering
- Log in to post comments
Backscatter communication (BSC) is emerging as the core technology for pervasive sustainable internet-of-things applications. However, owing to the resource-limitations of passive tags, this work targets at maximizing the achievable sum-backscattered-throughput by jointly optimizing the transceiver (TRX) design at the full-duplex multiantenna reader and backscattering coefficients (BC) at the single antenna tags.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views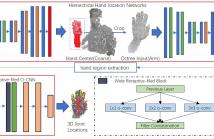
- Read more about A Novel Framework Of Hand Localization And Hand Pose Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel framework for hand localization and pose estimation from a single depth image. For hand localization, unlike most existing methods that using heuristic strategies, e.g. color segmentation, we propose Hierarchical Hand location Networks (HHLN) to estimate the hand location from coarse to fine in depth images, which is robust to the complex environment and efficient. It first applied at a low resolution octree of the whole depth image and produce coarse hand region and then constructs the hand region into a high resolution octree for fine location estimation.
poster_cheyunlong.pdf
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views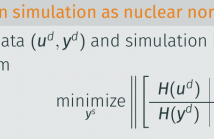
Applications of signal processing and control are classically model-based, involving a two-step procedure for modeling and design: first a model is built from given data, and second, the estimated model is used for filtering, estimation, or control. Both steps typically involve optimization problems, but the combination of both is not necessarily optimal, and the modeling step often ignores the ultimate design objective. Recently, data-driven alternatives are receiving attention, which employ a direct approach combining the modeling and design into a single step.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views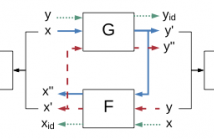
- Read more about Cycle-consistent adversarial networks for non-parallel vocal effort based speaking style conversion
- Log in to post comments
Speaking style conversion (SSC) is the technology of converting natural speech signals from one style to another. In this study, we propose the use of cycle-consistent adversarial networks (CycleGANs) for converting styles with varying vocal effort, and focus on conversion between normal and Lombard styles as a case study of this problem. We propose a parametric approach that uses the Pulse Model in Log domain (PML) vocoder to extract speech features. These features are mapped using the CycleGAN from utterances in the source style to the corresponding features of target speech.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views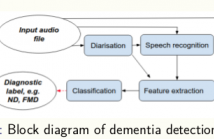
- Read more about COMPUTATIONAL COGNITIVE ASSESSMENT: INVESTIGATING THE USE OF AN INTELLIGENT VIRTUAL AGENT FOR THE DETECTION OF EARLY SIGNS OF DEMENTIA
- Log in to post comments
The ageing population has caused a marked increased in the number of people with cognitive decline linked with dementia. Thus, current diagnostic services are overstretched, and there is an urgent need for automating parts of the assessment process. In previous work, we demonstrated how a stratification tool built around an Intelligent Virtual Agent (IVA) eliciting a conversation by asking memory-probing questions, was able to accurately distinguish between people with a neuro-degenerative disorder (ND) and a functional memory disorder (FMD).
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
The cloud-based speech recognition/API provides developers or enterprises an easy way to create speech-enabled features in their applications. However, sending audios about personal or company internal information to the cloud, raises concerns about the privacy and security issues. The recognition results generated in cloud may also reveal some sensitive information. This paper proposes a deep polynomial network (DPN) that can be applied to the encrypted speech as an acoustic model. It allows clients to send their data in an encrypted form to the cloud to ensure that their data remains confidential, at mean while the DPN can still make frame-level predictions over the encrypted speech and return them in encrypted form. One good property of the DPN is that it can be trained on unencrypted speech features in the traditional way. To keep the cloud away from the raw audio and recognition results, a cloud-local joint decoding framework is also proposed. We demonstrate the effectiveness of model and framework on the Switchboard and Cortana voice assistant tasks with small performance degradation and latency increased comparing with the traditional cloud-based DNNs.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8683721
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Improving Speech Emotion Recognition with Unsupervised Representation Learning on Unlabeled Speech
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views
We investigate the use of entropy-regularized optimal transport (EOT) cost in developing generative models to learn implicit distributions. Two generative models are proposed. One uses EOT cost directly in an one-shot optimization problem and the other uses EOT cost iteratively in an adversarial game. The proposed generative models show improved performance over contemporary models on scores of sample based test.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views