- Transducers
- Spatial and Multichannel Audio
- Source Separation and Signal Enhancement
- Room Acoustics and Acoustic System Modeling
- Network Audio
- Audio for Multimedia
- Audio Processing Systems
- Audio Coding
- Audio Analysis and Synthesis
- Active Noise Control
- Auditory Modeling and Hearing Aids
- Bioacoustics and Medical Acoustics
- Music Signal Processing
- Loudspeaker and Microphone Array Signal Processing
- Echo Cancellation
- Content-Based Audio Processing

- Read more about Sparse Representation of Human Auditory System
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, three sparse models for the human auditory system are proposed. Biological studies shows that the haircells in the inner ear of the auditory system generate sparse codes from the output of cochlea filterbank. Here, we employ two mathematical sparse representation methods, which are Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) and K Singular Value Decomposition (K-SVD), in three different strategies for sparse representation of the output of cochlea filterbank that is modeled by a Gammatone filterbank.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about GREEDY APPROACHES TO FINDING A SPARSE COVER IN A SENSOR NETWORK WITHOUT LOCATION INFORMATION
- Log in to post comments
Modeling a location-unaware sensor network as a simplicial complex, where simplices correspond to cliques in the communication graph, has proven useful for solving a number of coverage problems under certain conditions using algebraic topology. Several approaches to finding a sparse cover for a fenced sensor network are considered, including calculating homology changes locally, strong collapsing, and Euler characteristic collapsing.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about Third dimension for measurement of multi user massive MIMO channels based on LTE advanced downlink
- Log in to post comments
We characterize third-dimension (3D) of channel measurements based on two dimension channel model with fully synchronize
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Action Classification from Motion Capture Data using Topological Data Analysis
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel framework for activity recognition from 3D motion capture data using topological data analysis (TDA). We extract point clouds describing the oscillatory patterns of body joints from the principal components of their time series using Taken's delay embedding. Topological persistence from TDA is exploited to extract topological invariants of the constructed point clouds. We propose a feature extraction method from persistence diagrams in order to generate robust low dimensional features used for classification of different activities.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views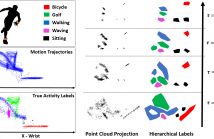
- Read more about Hierarchical Activity Clustering Analysis for Robust Graphical Structure Recovery
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we propose a hierarchical activity clustering methodology which incorporates the use of topological persistence analysis. Our clustering methodology captures the hierarchies present in the data and is therefore able to show the dependencies that exist between these activities. We make use of an aggregate persistence diagram to select robust graphical structures present within the dataset. These models are stable over a bound and provide accurate classification results.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Gotong Royong in NLP Research: A Mobile Tool for Collaborative Text Annotation in Indonesia
- Log in to post comments
The absence of manually annotated training data presents an obstacle for the development of machine-learning based NLP tools in Indonesia. Existing annotation tools lack a mobile-friendly interface which is a problem in Indonesia where most users access the internet using their smartphone. In this paper we propose the first mobile collaborative data annotation tool and evaluate it in an experiment involving 15 Indonesian students who annotated 1500 data records using their smartphones. Users confirmed
- Categories:
 70 Views
70 Views- Read more about On Training Bi-directional Neural Network Language Model with Noise Contrastive Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Although uni-directional recurrent neural network language
model(RNNLM) has been very successful, it’s hard to train a
bi-directional RNNLM properly due to the generative nature of
language model. In this work, we propose to train bi-directional
RNNLM with noise contrastive estimation(NCE), since the
properities of NCE training will help the model to acheieve
sentence-level normalization. Experiments are conducted on
two hand-crafted tasks on the PTB data set: a rescore task and
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about A Study on perceptual training of Japanese CSL Learner to Discriminate Mandarin Lexical Tones
- Log in to post comments
In process of learning Chinese as a second language (CSL), Japanese natives have difficulties in tone perception. Among the four Chinese lexical tones, the tone pairs Tone 1-Tone 2 and Tone 1-Tone 4 are problematic for Japanese CSL beginners. In order to help them develop efficiently discriminating capability of the tone pairs, we designed a hybrid perceptual training scheme which combined adaptive training and high variability phonetic training.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views