- Transducers
- Spatial and Multichannel Audio
- Source Separation and Signal Enhancement
- Room Acoustics and Acoustic System Modeling
- Network Audio
- Audio for Multimedia
- Audio Processing Systems
- Audio Coding
- Audio Analysis and Synthesis
- Active Noise Control
- Auditory Modeling and Hearing Aids
- Bioacoustics and Medical Acoustics
- Music Signal Processing
- Loudspeaker and Microphone Array Signal Processing
- Echo Cancellation
- Content-Based Audio Processing

- Read more about Acoustic Correlates and Gender Effects in Production and Perception of Japanese Polite Speech
- Log in to post comments
This study examines potential contribution of prosodic features and voice quality to the perception and production of Japanese polite speech as well as possible gender effects in politeness strategy.
Shi Shuju, Tsurutani Chiharu, Feng Xiaoli, Zhang Jinsong, Minematsu Nobuaki
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Automatic Detection of Rhythmic Patterns in Native and L2 Speech: Chinese, Japanese, and Japanese L2 Chinese
- Log in to post comments
This study explores possible contribution of speech rhythm to foreign accent. We conducted statistical analysis and realized automatic detection of rhythmic patterns on Mandarin Chinese, Japanese and Japanese second language learners (L2) of Chinese using interval-based and amplitude-based measures.
rhythm.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Applying Connectionist Temporal Classification Objective Function to Chinese Mandarin Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
This paper establishs CTC-based systems on Chinese Mandarin ASR task, three different level output units are explored: characters, context independent phonemes and context dependent phoneme. To make training stable we propose Newbob-Trn strategy, furthermore, blank label prior cost is proposed to improve the performance. Further, we establish the CTC-trained UniLSTM-RC model, which ensures the real-time requirement of an online system, meanwhile, brings performance gain on Chinese Mandarin ASR task.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views- Read more about The influence of syllable structure and prosodic strengthening on consonant production in Shanghai Chinese
- Log in to post comments
id201.pptx
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views- Read more about A REGRESSION APPROACH TO BINAURAL SPEECH SEGREGATION VIA DEEP NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a novel regression approach to binaural speech segregation based on deep neural network (DNN). In contrast to the conventional ideal binary mask (IBM) method using DNN with the interaural time difference (ITD) and interaural level difference (ILD) as the auditory features, the log-power spectra (LPS) features of target speech are directly predicted via a regression DNN model by concatenating the monaural LPS features and the binaural features as the input.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about The Design and Implementation of HMM-based Dai Speech Synthesis
- Log in to post comments
By far there are more than 1.2 million Dai compatriots using Dai language in Yunnan province,researching Dai speech synthesis has great significance in advancing the informationization of Dai.This paper researches the implementation of Dai speech synthesis by taking the HMM speech synthesis framework and STRAIGHT synthesizer into account.
In this paper,collection and selection of Dai text corpus,recording of speech corpus,text normalization,segmentation,Romanization and the implementation of acoustic model training are described.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Contributions of the Piriform Fossa of Female Speakers to Vowel Spectra
- Log in to post comments
The bilateral cavities of the piriform fossa are the side branches of the vocal tract and produce anti-resonance(s) in the transfer function. This effect has been known for male vocal tracts, but female data were few. This study investigates contributions of the piriform fossa to vowel spectra in female vocal tracts by means of MRI-based vocal-tract modeling and acoustic experiment with the water-filling technique. Results from three female subjects indicate that the piriform fossa generates one or two dips in the frequency region of 4-6 kHz.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views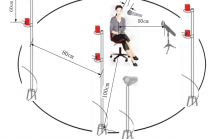
- Read more about A multi-channel/multi-speaker interactive 3D Audio-Visual Speech Corpus in Mandarin
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a multi-channel/multi-speaker 3D audiovisual
corpus for Mandarin continuous speech recognition and
other fields, such as speech visualization and speech synthesis.
This corpus consists of 24 speakers with about 18k utterances,
about 20 hours in total. For each utterance, the audio
streams were recorded by two professional microphones in
near-field and far-field respectively, while a marker-based 3D
facial motion capturing system with six infrared cameras was
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Long Short-term Memory Recurrent Neural Network based Segment Features for Music Genre Classification
- Log in to post comments
In the conventional frame feature based music genre
classification methods, the audio data is represented by
independent frames and the sequential nature of audio is totally
ignored. If the sequential knowledge is well modeled and
combined, the classification performance can be significantly
improved. The long short-term memory(LSTM) recurrent
neural network (RNN) which uses a set of special memory
cells to model for long-range feature sequence, has been
successfully used for many sequence labeling and sequence
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Mismatched Training Data Enhancement for Automatic Recognition of Children’s Speech using DNN-HMM
- Log in to post comments
The increasing profusion of commercial automatic speech recognition technology applications has been driven by big-data techniques, making use of high quality labelled speech datasets. Children’s speech displays greater time and frequency domain variability than typical adult speech, lacks the depth and breadth of training material, and presents difficulties relating to capture quality. All of these factors act to reduce the achievable performance of systems that recognise children’s speech.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views