- Read more about SAFE SCREENING FOR SPARSE REGRESSION WITH THE KULLBACK-LEIBLER DIVERGENCE
- Log in to post comments
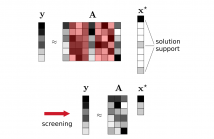
Safe screening rules are powerful tools to accelerate iterative solvers in sparse regression problems. They allow early identification of inactive coordinates (i.e., those not belonging to the support of the solution) which can thus be screened out in the course of iterations. In this paper, we extend the GAP Safe screening rule to the L1-regularized Kullback-Leibler divergence which does not fulfill the regularity assumptions made in previous works. The proposed approach is experimentally validated on synthetic and real count data sets.
- Categories:
 68 Views
68 Views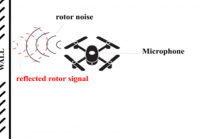
In this paper, we propose a method to estimate the proximity of an acoustic reflector, e.g., a wall, using ego-noise, i.e., the noise produced by the moving parts of a listening robot. This is achieved by estimating the times of arrival of acoustic echoes reflected from the surface. Simulated experiments show that the proposed non-intrusive approach is capable of accurately estimating the distance of a reflector up to 1 meter and outperforms a previously proposed intrusive approach under loud ego-noise conditions.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
A consensus based distributed algorithm to compute
the spectral radius of a network is proposed. The spectral radius
of the graph is the largest eigenvalue of the adjacency matrix, and
is a useful characterization of the network graph. Conventionally,
centralized methods are used to compute the spectral radius, which
involves eigenvalue decomposition of the adjacency matrix of the
underlying graph. Our distributed algorithm uses a simple update
rule to reach consensus on the spectral radius, using only local
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about TIME-DOMAIN CONCENTRATION AND APPROXIMATION OF COMPUTABLE BANDLIMITED SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
Turing computability deals with the question of what is theoretically computable on a digital computer, and hence is relevant whenever digital hardware is used. In this paper we study different possibilities to define computable bandlimited signals and systems. We consider a definition that uses finite Shannon sampling series as approximating functions and another that employs computable continuous functions together with an effectively computable time concentration. We discuss the advantages and drawbacks of both definitions and analyze the connections and differences.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about CONTRASTIVE SEPARATIVE CODING FOR SELF-SUPERVISED REPRESENTATION LEARNING
- Log in to post comments
To extract robust deep representations from long sequential modeling of speech data, we propose a self-supervised learning approach, namely Contrastive Separative Coding (CSC). Our key finding is to learn such representations by separating the target signal from contrastive interfering signals.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Joint optimization of spectrally co-existing multi-carrier radar and communication systems in cluttered environment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Low-Complexity Parameter Learning for OTFS Modulation Based Automotive Radar
- Log in to post comments
Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) as an emerging modulation technique in the 5G and beyond era exploits full time-frequency diversity and is robust against doubly-selective channels in high mobility scenarios. In this work, we consider an OTFS modulation based automotive joint radar-communication system and focus on the design of low-complexity parameter estimation algorithm for radar targets.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Switched Hawkes Processes
- Log in to post comments
Hawkes processes are a class of auto-regressive point processes that are commonly used in modeling data in which events tend to cluster and influence the likelihood of future events. Because of their ability to model and explain how events or processes can influence each other, Hawkes processes (and their multivariate extensions) have been applied in a variety of practical applications such as analyzing financial time series, communication networks, and biological networks, to name just a few.
icassp_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about ON THE ACCURACY LIMIT OF JOINT TIME-DELAY/DOPPLER/ACCELERATION ESTIMATION WITH A BAND-LIMITED SIGNAL
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
We address the problem of filtering out localized time-frequency components in signals. The problem is formulatedas a minimization of a suitable quadratic form, that involves adata fidelity term on the short-time Fourier transform outsidethe support of the undesired component, and an energy pe-nalization term inside the support. The minimization yields alinear system whose solution can be expressed in closed formusing Gabor multipliers.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views