
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about EMOTION RECOGNITION THROUGH INTEGRATING EEG AND PERIPHERAL SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
The inherent dependencies among multiple physiological signals are crucial for multimodal emotion recognition, but have not been thoroughly exploited yet. This paper propose to use restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM) to model such dependencies.Specifically, the visible nodes of RBM represent EEG and peripheral physiological signals, and thus the connections between visible nodes and hidden nodes capture the intrinsic relations among multiple physiological signals. The RBM also generate new representation from multiple physiological signals.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 ViewsThe inherent dependencies among video content, personal characteristics, and perceptual emotion are crucial for personalized video emotion tagging, but have not been thoroughly exploited. To address this, we propose a novel topic model to capture such inherent dependencies. We assume that there are several potential human factors, or “topics,” that affect the personal characteristics and the personalized emotion responses to videos.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about Disjunctive Normal Shape Boltzmann Machine
- Log in to post comments
Shape Boltzmann machine (a type of Deep Boltzmann machine) is a powerful tool for shape modelling; however, has some drawbacks in representation of local shape parts. Disjunctive Normal Shape Model (DNSM) is a strong shape model that can effectively represent local parts of objects. In this paper, we propose a new shape model based on Shape Boltzmann Machine and Disjunctive Normal Shape Model which we call Disjunctive Normal Shape Boltzmann Machine (DNSBM).
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views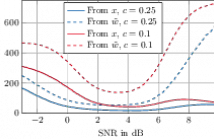
- Read more about Sequential Joint Signal Detection and Signal-to-Noise Ratio Estimation
- Log in to post comments
The sequential analysis of the problem of joint signal detection and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) estimation for a linear Gaussian observation model is considered. The problem is posed as an optimization setup where the goal is to minimize the number of samples required to achieve the desired (i) type I and type II error probabilities and (ii) mean squared error performance.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views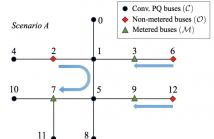
Power distribution grids are currently challenged by observability issues due to limited metering infrastructure. On the other hand, smart meter data, including local voltage magnitudes and power injections, are collected at grid nodes with renewable generation and demand response programs. A power flow-based approach using these data is put forth here to infer the unknown power injections at non-metered grid nodes.
ICASSP1.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about Performance Trade-off in an Adaptive IEEE 802.11ad Waveform Design for a Joint Automotive Radar and Communication System
- Log in to post comments
The IEEE 802.11ad waveform can be used for automotive radar by exploiting the Golay complementary sequences in the preamble of a frame. The performance of radar, however, is limited by the preamble structure. In this paper, we propose an adaptive preamble design that permits a trade-off between radar parameters’ estimation accuracy and communication rate. To quantify this trade-off, we propose a minimum mean square error (MMSE) metric based on rate distortion theory.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views- Read more about Hybrid Precoding Using Long-term Channel Statistics for Massive MIMO Systems
- Log in to post comments
Hybrid analog/digital precoding in the downlink of multiuser massive MIMO systems can reduce the number of RF chains hence reducing total cost and improving power efficiency. Having few RF chains, however, makes it difficult for a base station to acquire instantaneous channel state information across all antennas. We develop a hybrid technique that uses only long-term (slowly changing) channel statistics in computing the analog precoding matrix. The proposed analog precoder is designed to maximize signal-to-leakage-plusnoise ratio (SLNR) when combined with a baseband precoder.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views- Read more about Super-resolution delay-Doppler estimation for sub-Nyquist radar via atomic norm minimization
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP2017.pdf
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views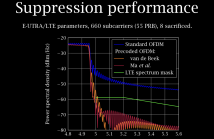
- Read more about Orthogonal Precoding for Sidelobe Suppression in DFT-Based Systems Using Block Reflectors
- Log in to post comments
Sidelobe suppression has always been an important part of crafting communications signals to keep interference with users of adjacent spectrum to a minimum. Systems based on the discrete Fourier transform, such as orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) and single-carrier frequency-division multiple access (SC-FDMA) are especially prone to out-of-band power leakage. Although many techniques have been proposed to suppress sidelobes in DFT-based systems, a satisfactory balance between computational complexity and out-of-band power leakage has remained elusive.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views