
ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2017 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics. Visit ICASSP 2017
- Read more about JOINT CHANNEL AND CARRIER FREQUENCY ESTIMATION FOR M-ARY CPM OVER FREQUENCY-SELECTIVE CHANNEL USING PAM DECOMPOSITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views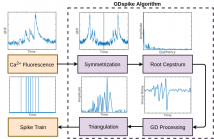
- Read more about GDSPIKE: AN ACCURATE SPIKE ESTIMATION ALGORITHM FROM NOISY CALCIUM FLUORESCENCE SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
Accurate estimation of spike train from calcium (Ca2+) fluorescence signals is challenging owing to significant fluctuations of fluorescence level. This paper proposes a non-model-based approach for spike train inference using group delay (GD) analysis. It primarily exploits the property that change in Ca2+ fluorescence corresponding to a spike can be characterized by an onset, an attack, and a decay. The proposed algorithm, GDspike, is compared with state-of-the-art systems on five datasets. F-measure is best for GDspike (41%) followed by STM (40%), MLspike (39%), and Vogelstein (35%).
main_jilt.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about APPROXIMATE SIMULATION OF LINEAR CONTINUOUS TIME MODELS DRIVEN BY ASYMMETRIC STABLE LÉVY PROCESSES
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we extend to the multidimensional case the modified Poisson series representation of linear stochastic processes driven by $\alpha$-stable innovations. The latter has been recently introduced in the literature and it involves a Gaussian approximation of the residuals of the series, via the exact characterization of their moments. This allows for Bayesian techniques for parameter or state inference that would not be available otherwise, due to the lack of a closed-form likelihood function for the $\alpha$-stable distribution.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views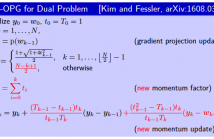
- Read more about Accelerated dual gradient-based methods for total variation image denoising/deblurring problems
- Log in to post comments
icassp-kim.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about LOW-RANK AND SPARSE SOFT TARGETS TO LEARN BETTER ! DNN ACOUSTIC MODELS
- Log in to post comments
Conventional deep neural networks (DNN) for speech acoustic modeling rely on Gaussian mixture models (GMM) and hidden Markov model (HMM) to obtain binary class labels as the targets for DNN training. Subword classes in speech recognition systems correspond to context-dependent tied states or senones. The present work addresses some limitations of GMM-HMM senone alignments for DNN training. We hypothesize that the senone probabilities obtained from a DNN trained with binary labels can provide more accurate targets to learn better acoustic models.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised learning of asymmetric high-order autoregressive stochastic volatility model
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a new estimation algorithm specifically designed for the latent high-order autoregressive models. It implements the concept of the filter-based maximum likelihood. Our approach is fully deterministic and is less computationally demanding than the traditional Monte Carlo Markov chain techniques. The simulation experiments confirm the interest of our approach.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views- Read more about An LSTM-CTC based verification system for proxy-word based OOV keyword search
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about An LSTM-CTC based verification system for proxy-word based OOV keyword search
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views