
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Improved Algorithms for Differentially private Orthogonal Tensor Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Tensor decompositions have applications in many areas including signal processing, machine learning, computer vision and neuroscience. In this paper, we propose two new differentially private algorithms for orthogonal decomposition of symmetric tensors from private or sensitive data; these arise in applications such as latent variable models. Differential privacy is a formal privacy framework that guarantees protections against adversarial inference.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Differentially private Distributed Principal Component Analysis
- Log in to post comments
Differential privacy is a cryptographically-motivated formal privacy definition that is robust against strong adversaries. The principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm is frequently used in signal processing, machine learning, and statistics pipelines. In many scenarios, private or sensitive data is distributed across different sites: in this paper we propose a differentially private distributed PCA scheme to enable collaborative dimensionality reduction.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING THE USE OF GROUP DELAY FOR GENERALISED VTS BASED NOISE COMPENSATION
- Log in to post comments
In earlier work we studied the effect of statistical normalisation for phase-based features and observed it leads to a significant robustness improvement. This paper explores the extension of the generalised Vector Taylor Series (gVTS) noise compensation approach to the group delay (GD) domain. We discuss the problems it presents, propose some solutions and derive the corresponding formulae. Furthermore, the effects of additive and channel noise in the GD domain were studied.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about FAST ROBUST TRACKING VIA DOUBLE CORRELATION FILTER FORMULATION
- Log in to post comments
Over the past few years, fast and robust trackers based on Kernelized Correlation Filters have shown top notch performance on the Visual Object Tracking challenge. However there is still scope for obtaining higher performance through the use of reasonable approximations that can easily be shown to work through empirical methods. We study some variants derived from the Discriminative Scale Space Tracker and show significant improvement in tracking performance.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Common and Individual Feature Extraction using Tensor Decompositions: A Remedy for the Curse of Dimensionality?
- Log in to post comments
A novel method for common and individual feature analysis from exceedingly large-scale data is proposed, in order to ensure the tractability of both the computation and storage and thus mitigate the curse of dimensionality, a major bottleneck in modern data science. This is achieved by making use of the inherent redundancy in so-called multi-block data structures, which represent multiple observations of the same phenomenon taken at different times, angles or recording conditions.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views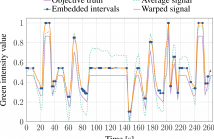
- Read more about A Novel Method for Human Bias Correction of Continuous-time Annotations
- Log in to post comments
Human annotations are of integral value in human behavior studies and in particular for the generation of ground truth for behavior prediction using various machine learning methods. These often subjective human annotations are especially required for studies involving measuring and predicting hidden mental states (e.g. emotions) that cannot effectively be measured or assessed by other means. Human annotations are noisy and prone to the influence of several factors including personal bias, task ambiguity, environmental distractions, and health state.
- Categories:
 93 Views
93 Views
- Read more about MULTI-VIEW AUDIO-ARTICULATORY FEATURES FOR PHONETIC RECOGNITION ON RTMRI-TIMIT DATABASE
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate the use of articulatory informa-
tion, and more specifically real time Magnetic Resonance
Imaging (rtMRI) data of the vocal tract, to improve speech
recognition performance. For the purpose of our experiments,
we use data from the rtMRI-TIMIT database. Firstly, Scale
Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) features are extracted for
each video frame. Afterwards, the SIFT descriptors of each
frame are transformed to a single histogram per picture, by
using the Bag of Visual Words methodology. Since this kind
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Framework For Evaluation Of Sound Event Detection In Web Videos
- Log in to post comments
The largest source of sound events is web videos. Most videos lack sound event labels at segment level, however, a significant number of them do respond to text queries, from a match found using metadata by search engines. In this paper we explore the extent to which a search query can be used as the true label for detection of sound events in videos. We present a framework for large-scale sound event recognition on web videos. The framework crawls videos using search queries corresponding to 78 sound event labels drawn from three datasets.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about A CONVERSATIONAL NEURAL LANGUAGE MODEL FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION IN DIGITAL ASSISTANTS
- Log in to post comments
Speech recognition in digital assistants such as Google Assistant can
potentially benefit from the use of conversational context consisting of user
queries and responses from the agent. We explore the use of recurrent,
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), neural language models (LMs) to model the conversations
in a digital assistant. Our proposed methods effectively capture the context of
previous utterances in a conversation without modifying the underlying LSTM
architecture. We demonstrate a 4% relative improvement in recognition performance
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views