
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Unsupervised Image Segmentation by Backpropagation
- Log in to post comments
We investigate the use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for unsupervised image segmentation. As in the case of supervised image segmentation, the proposed CNN assigns labels to pixels that denote the cluster to which the pixel belongs. In the unsupervised scenario, however, no training images or ground truth labels of pixels are given beforehand. Therefore, once when a target image is input, we jointly optimize the pixel labels together with feature representations while their parameters are updated by gradient descent.
- Categories:
 875 Views
875 Views
- Read more about Speaker Invariant Feature Extraction for Zero-Resource Languages with Adversarial Learning
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel type of representation learning to obtain a speaker invariant feature for zero-resource languages. Speaker adaptation is an important technique to build a robust acoustic model. For a zero-resource language, however, conventional model-dependent speaker adaptation methods such as constrained maximum likelihood linear regression are insufficient because the acoustic model of the target language is not accessible. Therefore, we introduce a model-independent feature extraction based on a neural network.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views- Read more about Joint Estimation of the Room Geometry and Modes with Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Acoustical behavior of a room for a given position of microphone and sound source is usually described using the room impulse response. If we rely on the standard uniform sampling, the estimation of room impulse response for arbitrary positions in the room requires a large number of measurements. In order to lower the required sampling rate, some solutions have emerged that exploit the sparse representation of the room wavefield in the terms of plane waves in the low-frequency domain. The plane wave representation has a simple form in rectangular rooms.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views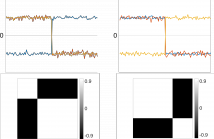
- Read more about EVALUATING MODELS OF DYNAMIC FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY USING PREDICTIVE CLASSIFICATION ACCURACY
- Log in to post comments
Dynamic functional connectivity has become a prominent approach for tracking the changes of macroscale statistical dependencies between regions in the brain. Effective parametrization of these statistical dependencies, referred to as brain states, is however still an open problem. We investigate different emission models in the hidden Markov model framework, each representing certain assumptions about dynamic changes in the brain.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about A MULTI-CAMERA DEEP NEURAL NETWORK FOR DETECTING ELEVATED ALERTNESS IN DRIVERS
- Log in to post comments
We present a system for the detection of elevated levels of driver alertness in driver-facing video captured from multiple viewpoints. This problem is important in automotive safety as a helpful feedback signal to determine driver engagement and as a means of automatically flagging anomalous driving events. We generated a dataset of videos from 25 participants overseeing an hour each of driving sequences in a simulator consisting of a mixture of normal and near-miss driving events.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Grid-Free Direction-of-Arrival Estimation with Compressed Sensing and Arbitrary Antenna Arrays
- Log in to post comments
We study the problem of direction of arrival estimation for arbitrary antenna
arrays. We formulate it as a continuous line spectral estimation problem and solve it under
a sparsity prior without any gridding assumptions. Moreover, we incorporate the
array's beampattern in form of the Effective Aperture Distribution Function
(EADF), which allows to use arbitrary (synthetic as well as measured) antenna
arrays. This generalizes known atomic norm based grid-free DOA estimation methods (that
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about CATSEYES: Categorizing Seismic structures with tessellated scattering wavelet networks
- Log in to post comments
As field seismic data sizes are dramatically increasing toward exabytes, automating the labeling of ``structural monads'' --- corresponding to geological patterns and yielding subsurface interpretation --- in a huge amount of available information would drastically reduce interpretation time. Since customary designed features may not account for gradual deformations observable in seismic data, we propose to adapt the wavelet-based scattering network methodology with a tessellation of geophysical images.
- Categories:
 230 Views
230 Views
- Read more about A PARALLEL FUSION APPROACH TO PIANO MUSIC TRANSCRIPTION BASED ON CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Ear-EEG for Detecting Inter-brain Synchronisation in Continuous Cooperative Multi-person Scenarios
- Log in to post comments
The hyperscanning method simultaneously acquires and relates
cerebral data from two participants while performing
cooperative activities. The aim of this work is to evaluate
the performance of our novel EEG recording concept,
termed ear-EEG, against on-scalp EEG as an alternative,
user-friendly data acquisition approach for hyperscanning, in
the task of identifying the most robust, EEG subbands for
inter-individual neuronal synchrony detection in cooperative
multi-player gaming. This is achieved through the estimation
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about A Novel Learnable Dictionary Encoding Layer for End-to-End Language Identification
- Log in to post comments
A novel learnable dictionary encoding layer is proposed in this paper for end-to-end language identification. It is inline with the conventional GMM i-vector approach both theoretically and practically. We imitate the mechanism of traditional GMM training and Supervector encoding procedure on the top of CNN. The proposed layer can accumulate high-order statistics from variable-length input sequence and generate an utterance level fixed-dimensional vector representation.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views