
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about The Direction Cosine Matrix Algorithm in Fixed-Point: Implementation and Analysis
- Log in to post comments
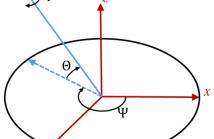
Inertial navigation allows tracking and updating the position and orientation of a moving object based on accelerometer and gyroscope data without external positioning aid, such as GPS. Therefore, inertial navigation is an essential technique for, e.g., indoor positioning. As inertial navigation is based on integration of acceleration vector components, computation errors accumulate and make the position and orientation estimate drift.
poster_mbc.pdf
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 Views

- Read more about On the Fourier Representation of Computable Continuous Signals
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about FRI MODELLING OF FOURIER DESCRIPTORS
- Log in to post comments
Fourier descriptors are used to parametrically represent closed contours. In practice, a finite set of Fourier descriptors can model a large class of smooth contours. In this paper, we propose a method for estimating the Fourier descriptors of a given contour from its partial samples. We take a sampling-theoretic approach to model the x and y coordinate functions of the shape and express them as a sum of weighted complex exponentials, which belong to the class of finite-rate-of-innovation (FRI) signals. The weights represent the Fourier descriptors of the shape.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Semi-supervised Monaural Singing Voice Separation with a Masking Network Trained on Synthetic Mixtures - Poster
- Log in to post comments
We study the problem of semi-supervised singing voice separation, in which the training data contains a set of samples of mixed music (singing and instrumental) and an unmatched set of instrumental music. Our solution employs a single mapping function g, which, applied to a mixed sample, recovers the underlying instrumental music, and, applied to an instrumental sample, returns the same sample. The network g is trained using purely instrumental samples, as well as on synthetic mixed samples that are created by mixing reconstructed singing voices with random instrumental samples.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
Despite significant advancements of deep learning on separating speech sources mixed in a single channel, same gender speaker mix, i.e., male-male or female-female, is still more difficult to separate than the case of opposite gender mix. In this study, we propose a pitch-aware speech separation approach to improve the speech separation performance.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views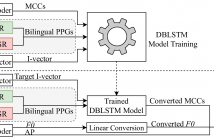
- Read more about CROSS-LINGUAL VOICE CONVERSION WITH BILINGUAL PHONETIC POSTERIORGRAM AND AVERAGE MODELING
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a cross-lingual voice conversion approach using bilingual Phonetic PosteriorGram (PPG) and average modeling. The proposed approach makes use of bilingual PPGs to represent speaker-independent features of speech signals from different languages in the same feature space. In particular, a bilingual PPG is formed by stacking two monolingual PPG vectors, which are extracted from two monolingual speech recognition systems. The conversion model is trained to learn the relationship between bilingual PPGs and the corresponding acoustic features.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views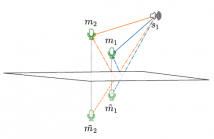
- Read more about MIRAGE: 2D sound source localization using microphone pair augmentation with echoes
- Log in to post comments
It is commonly observed that acoustic echoes hurt perfor-mance of sound source localization (SSL) methods. We in-troduce the concept of microphone array augmentation withechoes (MIRAGE) and show how estimation of early-echocharacteristics can in fact benefit SSL. We propose a learning-based scheme for echo estimation combined with a physics-based scheme for echo aggregation.
- Categories:
 150 Views
150 Views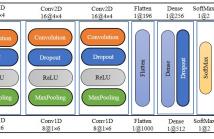
- Read more about Short-Segment Heart Sound Classification Using an Ensemble of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a framework based on deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for automatic heart sound classification using short-segments of individual heart beats. We design a 1D-CNN that directly learns features from raw heart-sound signals, and a 2D-CNN that takes inputs of two-dimensional time-frequency feature maps based on Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients. We further develop a time-frequency CNN ensemble (TF-ECNN) combining the 1D-CNN and 2D-CNN based on score-level fusion of the class probabilities.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views