
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Revisiting and improving semi-supervised learning: a large dimensional approach
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about A LARGE SCALE ANALYSIS OF LOGISTIC REGRESSION: ASYMPTOTIC PERFORMANCE AND NEW INSIGHTS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Analysis Dictionary Learning: An Efficient and Discriminative Solution
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views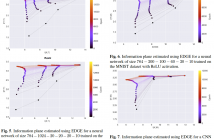
- Read more about Scalable Mutual Information Estimation using Dependence Graphs
- Log in to post comments
The Mutual Information (MI) is an often used measure of dependency between two random variables utilized in informa- tion theory, statistics and machine learning. Recently several MI estimators have been proposed that can achieve paramet- ric MSE convergence rate. However, most of the previously proposed estimators have high computational complexity of at least O(N2). We propose a unified method for empirical non-parametric estimation of general MI function between random vectors in Rd based on N i.i.d. samples.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views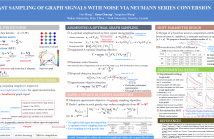
- Read more about Fast Sampling of Graph Signals with Noise via Neumann Series Conversion
- Log in to post comments
Graph sampling with independent noise towards minimum mean square error (MMSE)
leads to the known A-optimality criterion, which is computation-intensive to
evaluate and NP-hard to optimize. In this paper, we propose a new low complexity
sampling strategy based on Neumann series that circumvents large matrix
inversion and eigen-decomposition. We first prove that a DC-shifted A-optimality
criterion is equivalent to an objective computed using the inverse of a
sub-matrix of an ideal graph low-pass (LP) filter. The LP filter matrix can be
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Generalized Boundary Detection Using Compression-Based Analytics
- Log in to post comments
We present a new method for boundary detection within sequential data using compression-based analytics. Our approach is to approximate the information distance between two adjacent sliding windows within the sequence. Large values in the distance metric are indicative of boundary locations. A new algorithm is developed, referred to as sliding information distance (SLID), that provides a fast, accurate, and robust approximation to the normalized information distance. A modified smoothed z-score algorithm is used to locate peaks in the distance metric, indicating boundary locations.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Complementary sequence encoding for 1D and 2D constant-modulus OFDM transmission at millimeter wave frequencies
- Log in to post comments
This paper develops a method for constructing an OFDM signal from a pair of complementary sequences so that the resulting signal is constant-modulus. A recursive method of constructing complementary sequences is developed such that the length of the signal grows linearly with the number of information symbols encoded. The constant-modulus property is exploited at each stage of the backwards symbol-decoding iteration through simple means to progressively reduce noise.
ICASSPposter.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about PRE-TRAINING OF SPEAKER EMBEDDINGS FOR LOW-LATENCY SPEAKER CHANGE DETECTION IN BROADCAST NEWS
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we investigate pre-training of neural network based speaker embeddings for low-latency speaker change detection. Our proposed system takes two speech segments, generates embeddings using shared Siamese layers and then classifies the concatenated embeddings depending on whether they are spoken by the same speaker. We investigate gender classification, contrastive loss and triplet loss based pre-training of the embedding layers and also joint training of the embedding layers along with a same/different classifier.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views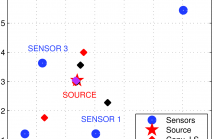
- Read more about A Data-Selective LS Solution to TDOA-based Source Localization
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, the localization of an emitter based on Time Difference of Arrival (TDoA) has been investigated. The classical least-squares (LS) algorithm, with a limited number of TDoA measurements, has been utilized for obtaining a closed-form solution to the source localization problem. Recently, an extension of the classical LS algorithm has been employed in an attempt to improve the precision of the localization technique by using a larger set of TDoA estimates.
PosterTDOA.pdf
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views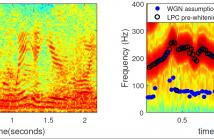
- Read more about A Study on how Pre-Whitening Influences Fundamental Frequency Estimation
- Log in to post comments
This paper deals with the influence of pre-whitening for the task of fundamental frequency estimation in noisy conditions. Parametric fundamental frequency estimators commonly assume that the noise is white and Gaussian and, therefore, they are only statistically efficient under those conditions. The noise is coloured in many practical applications and this will often result in problems of misidentifying an integer divisor or multiple of the true fundamental frequency (i.e., octave errors).
- Categories:
 102 Views
102 Views