
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
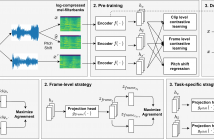
- Read more about SELF-SUPERVISED LEARNING METHOD USING MULTIPLE SAMPLING STRATEGIES FOR GENERAL-PURPOSE AUDIO REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
We propose a self-supervised learning method using multiple sampling strategies to obtain general-purpose audio representation. Multiple sampling strategies are used in the proposed method to construct contrastive losses from different perspectives and learn representations based on them. In this study, in addition to the widely used clip-level sampling strategy, we introduce two new strategies, a frame-level strategy and a task-specific strategy.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about THE SECOND DICOVA CHALLENGE: DATASET AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF COVID-19 USING ACOUSTICS
- Log in to post comments
The Second Diagnosis of COVID-19 using Acoustics (DiCOVA) Challenge aimed at accelerating the research in acoustics based detection of COVID-19, a topic at the intersection of acoustics, signal processing, machine learning, and healthcare. This paper presents the details of the challenge, which was an open call for researchers to analyze a dataset of audio recordings consisting of breathing, cough and speech signals. This data was collected from individuals with and without COVID-19 infection, and the task in the challenge was a two-class classification.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about THE SECOND DICOVA CHALLENGE: DATASET AND PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF COVID-19 USING ACOUSTICS
- Log in to post comments
The Second Diagnosis of COVID-19 using Acoustics (DiCOVA) Challenge aimed at accelerating the research in acoustics based detection of COVID-19, a topic at the intersection of acoustics, signal processing, machine learning, and healthcare. This paper presents the details of the challenge, which was an open call for researchers to analyze a dataset of audio recordings consisting of breathing, cough and speech signals. This data was collected from individuals with and without COVID-19 infection, and the task in the challenge was a two-class classification.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about NEWS RECOMMENDATION VIA MULTI-INTEREST NEWS SEQUENCE MODELLING
- Log in to post comments
A session-based news recommender system recommends the next news to a user by modeling the potential interests embedded in a sequence of news read/clicked by her/him in a session. Generally, a user's interests are diverse, namely there are multiple interests corresponding to different types of news, e.g., news of distinct topics, within a session. However, most of existing methods typically overlook such important characteristic and thus fail to distinguish and model the potential multiple interests of a user, impeding accurate recommendation of the next piece of news.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Progressive-Granularity Retrieval via Hierarchical Feature Alignment for Person Re-Identification
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Deep Object Detection With Example Attribute Based Prediction Modulation
- Log in to post comments
Deep object detectors suffer from the gradient contribution imbalance during training. In this paper, we point out that such imbalance can be ascribed to the imbalance in example attributes, e.g., difficulty and shape variation degree. We further propose example attribute based prediction modulation (EAPM) to address it. In EAPM, first, the attribute of an example is defined by the prediction and the corresponding ground truth. Then, a modulating factor w.r.t the example attribute is introduced to modulate the prediction error.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about RawNeXt: Speaker verification system for variable-duration utterances with deep layer aggregation and extended dynamic scaling policies
- Log in to post comments
Despite achieving satisfactory performance in speaker verification using deep neural networks, variable-duration utterances remain a challenge that threatens the robustness of systems. To deal with this issue, we propose a speaker verification system called RawNeXt that can handle input raw waveforms of arbitrary length by employing the following two components: (1) A deep layer aggregation strategy enhances speaker information by iteratively and hierarchically aggregating features of various time scales and spectral channels output from blocks.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Category-Adaptive Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views