
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about "DYNAMIC RESOURCEOPTIMIZATION FORADAPTIVE FEDERATED LEARNING EMPOWERED BY RECONFIGURABLE INTELLIGENT SURFACES" Slides
- Log in to post comments
The aim of this work is to propose a novel dynamic resource allocation strategy for adaptive Federated Learning (FL), in the context of beyond 5G networks endowed with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs). Due to time-varying wireless channel conditions, communication resources (e.g., set of transmitting devices, transmit powers, bits), computation parameters (e.g., CPU cycles at devices and at server) and RISs reflectivity must be optimized in each communication round, in order to strike the best trade-off between power, latency, and performance of the FL task.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views

- Read more about Data-Driven Algorithms for Gaussian Measurement Matrix Design in Compressive Sensing
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we provide two data-driven algorithms for learning compressive sensing measurement matrices with Gaussian entries. In contrast to the ubiquitous i.i.d.~Gaussian design, we associate different variances with different signal entries, so that we may utilize training data to focus more energy on the ``most important'' parts of the signal.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about MULTI-QUERY MULTI-HEAD ATTENTION POOLING AND INTER-TOPK PENALTY FOR SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes the multi-query multi-head attention (MQMHA)
pooling and inter-topK penalty methods which were first proposed in
our submitted system description for VoxCeleb speaker recognition
challenge (VoxSRC) 2021. Most multi-head attention pooling mechanisms either attend to the whole feature through multiple heads or
attend to several split parts of the whole feature. Our proposed
MQMHA combines both these two mechanisms and gain more
diversified information. The margin-based softmax loss functions
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views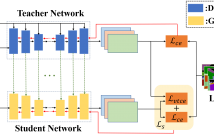
RGB-D semantic segmentation is attracting wide attention due to its better performance than conventional RGB methods. However, most of RGB-D semantic segmentation methods need to acquire the real depth information for segmenting RGB images effectively. Therefore, it is extremely challenging to take full advantage of RGB-D semantic segmentation methods for segmenting RGB images without the depth input.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about CARINA – A CORPUS OF ALIGNED GERMAN READ SPEECH INCLUDING ANNOTATIONS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents the semi-automatically created Corpus of Aligned Read Speech Including Annotations (CARInA), a speech corpus based on the German Spoken Wikipedia Corpus (GSWC). CARInA tokenizes, consolidates and organizes the vast, but rather unstructured material contained in GSWC. The contents are grouped by annotation completeness, and extended by canonic, morphosyntactic and prosodic annotations. The annotations are provided in BPF and TextGrid format.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
The paper deals with the state estimation of nonlinear stochastic dynamic systems with special attention on a grid-based numerical solution to the Bayesian recursive relations, the point-mass filter (PMF).
In the paper, a novel functional decomposition of the transient density describing the system dynamics is proposed.
The decomposition is based on a non-negative matrix factorization and separates the density into functions of the future and current states.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
Convolutional Neural Networks have been extensively used for solving many vision problems. However, due to high memory and computational requirements, deployment of these models on edge devices is limited. Many embedded friendly models such as MobileNet, ShuffleNet, SqueezeNet, and many more are proposed to serve this purpose. But these models are still not compact enough to deploy on edge devices. The popular metric-based pruning methods (which are aimed at pruning insignificant and redundant filters) could achieve limited compression for embedded friendly models such as MobileNet.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about KLM
- Log in to post comments
Structured Tucker tensor decomposition models complete or incomplete multiway data sets (tensors), where the core tensor and the factor matrices can obey different constraints. The model includes block-term decomposition or canonical polyadic decomposition as special cases. We propose a very flexible optimization method for the structured Tucker decomposition problem, based on the second-order Levenberg-Marquardt optimization, using an approximation of the Hessian matrix by the Krylov subspace method. An algorithm with limited sensitivity of the decomposition is included.
slidy22.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views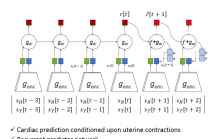
- Read more about Contrastive Predictive Coding for anomaly detection of fetal health from the cardiotocogram
- Log in to post comments
Fetal well-being during labor is currently assessed by medical professionals through visual interpretation of the cardiotocogram (CTG), a simultaneous recording of Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) and Uterine Contractions (UC). This method is disputed due to high inter- and intra-observer variability and a resulting increase in the number of unnecessary interventions. A method for computerized interpretation of the CTG, based on Contrastive Predictive Coding (CPC) is presented here.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views