
IEEE ICASSP 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2023 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about MEETING ACTION ITEM DETECTION WITH REGULARIZED CONTEXT MODELING
- Log in to post comments
Meetings are increasingly important for collaborations. Action items in meeting transcripts are crucial for managing post-meeting to-do tasks, which usually are summarized laboriously.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about MUG: A General Meeting Understanding And Generation Benchmark
- Log in to post comments
Listening to long video/audio recordings from video conferencing and online courses for acquiring information is extremely inefficient. Even after ASR systems transcribe recordings into long-form spoken language documents, reading ASR transcripts only partly speeds up seeking information. It has been observed that a range of NLP applications, such as keyphrase extraction, topic segmentation, and summarization, significantly improve users' efficiency in grasping important information.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views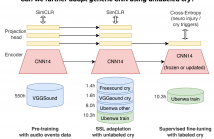
- Read more about Self-supervised learning for infant cry analysis
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we explore self-supervised learning (SSL) for analyzing a first-of-its-kind database of cry recordings containing clinical indications of more than a thousand newborns. Specifically, we target cry-based detection of neurological injury as well as identification of cry triggers such as pain, hunger, and discomfort.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views- Read more about Calibrating AI Models for Few-Shot Demodulation via Conformal Prediction
- Log in to post comments
Artificial Intelligent (AI) tools can be useful to address model deficits in the design of communication systems. However, conventional learning-based AI algorithms yield poorly calibrated decisions, unabling to quantify their outputs uncertainty. While Bayesian learning can enhance calibration by capturing epistemic uncertainty caused by limited data availability, formal calibration guarantees only hold under strong assumptions about the ground-truth, unknown, data generation mechanism.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Improved Deep Speaker Localization and Tracking: Revised Training Paradigm and Controlled Latency
- Log in to post comments
Even without a separate tracking algorithm, the directions of arrival (DOAs) of moving talkers can be estimated with a deep neural network (DNN) when the movement trajectories used for training allow the generalization to real signals. Previously, we proposed a framework for generating training data with time-variant source activity and sudden DOA changes. Slowly moving sources could be seen as a special case thereof, but were not explicitly modeled. In this paper, we extend this framework by using small jumps between neighboring discrete DOAs to simulate gradual movements.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views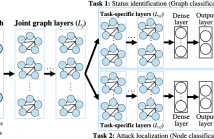
- Read more about A Graph Neural Network Multi-Task Learning-Based Approach for Detection and Localization of Cyberattacks in Smart Grids
- Log in to post comments
False data injection attacks (FDIAs) on smart power grids' measurement data present a threat to system stability. When malicious entities launch cyberattacks to manipulate the measurement data, different grid components will be affected, which leads to failures. For effective attack mitigation, two tasks are required: determining the status of the system (normal operation/under attack) and localizing the attacked bus/power substation. Existing mitigation techniques carry out these tasks separately and offer limited detection performance.
- Categories:
 64 Views
64 Views
- Read more about DEEP LOW LIGHT IMAGE ENHANCEMENT VIA MULTI-SCALE RECURSIVE FEATURE ENHANCEMENT AND CURVE ADJUSTMENT
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Photographs taken in low-illumination environment have a low signal-to-noise ratio and impaired visual quality. Enhancing low-light images tends to amplify noise. To address this problem, we propose a Multi-Scale Recursive Feature Enhancement (MSRFE) network for low light image enhancement. The MSRFE network consists of several Feature Enhancement (FE) blocks which are applied to enhance the multi-scale image feature and remove the noise recursively in each scale residual map between adjacent scale feature.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about TOWARDS IMPROVED ROOM IMPULSE RESPONSE ESTIMATION FOR SPEECH RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel approach for blind room impulse response (RIR) estimation systems in the context of a downstream application scenario, far-field automatic speech recognition (ASR). We first draw the connection between improved RIR estimation and improved ASR performance, as a means of evaluating neural RIR estimators.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Cross-site Generalization for imbalanced epileptic classification
- Log in to post comments
Recently, many studies have been conducted on automated epileptic seizures detection. However, few of these techniques are applied in clinical settings for several reasons. One of them is the imbalanced nature of the seizure detection task. Additionally, the current detection techniques do not really generalize to other patient populations. To address these issues, we present in this paper a hybrid CNN-LSTM model robust to cross-site variability. We investigate the use of data augmentation (DA) methods as an efficient tool to solve imbalanced training problems.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Cross-site Generalization for imbalanced epileptic classification
- Log in to post comments
Recently, many studies have been conducted on automated epileptic seizures detection. However, few of these techniques are applied in clinical settings for several reasons. One of them is the imbalanced nature of the seizure detection task. Additionally, the current detection techniques do not really generalize to other patient populations. To address these issues, we present in this paper a hybrid CNN-LSTM model robust to cross-site variability. We investigate the use of data augmentation (DA) methods as an efficient tool to solve imbalanced training problems.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views