
IEEE ICASSP 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2023 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
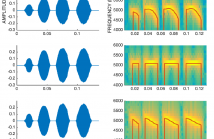
- Read more about ANALYSIS AND RE-SYNTHESIS OF NATURAL CRICKET SOUNDS ASSESSING THE PERCEPTUAL RELEVANCE OF IDIOSYNCRATIC PARAMETERS
- Log in to post comments
Cricket sounds are usually regarded as pleasant and, thus, can be used as suitable test signals in psychoacoustic experiments assessing the human listening acuity to specific temporal and spectral features. In addition, the simple structure of cricket sounds makes them prone to reverse engineering such that they can be analyzed and re-synthesized with desired alterations in their defining parameters.
poster_AJF.pdf
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Applying Symmetrical Component Transform for Industrial Appliance Classification in Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring
- Log in to post comments
Slides.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
End-to-End Spoken Language Understanding models are generally evaluated according to their overall accuracy, or separately on (a priori defined) data subgroups of interest.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about MaskDUL: Data Uncertainty Learning in Masked Face Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Since mask occlusion causes plentiful loss of facial feature, Masked Face Recognition (MFR) is a challenging image processing task, and the recognition results are susceptible to noise. However, existing MFR methods are mostly deterministic point embedding models, which are limited in representing noise images. Moreover, Data Uncertainty Learning (DUL) fails to achieve reasonable performance in MFR.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about MULTIMODAL EMOTION RECOGNITION BASED ON DEEP TEMPORAL FEATURES USING CROSS-MODAL TRANSFORMER AND SELF-ATTENTION
- Log in to post comments
Multimodal speech emotion recognition (MSER) is an emerging and challenging field of research due to its more robust characteristics than unimodal. However, in multimodal approaches, the interactive relations for model building using different modalities of speech representations for emotion recognition have not been well investigated yet. To address this issue, we introduce a new approach to capturing the deep temporal features of audio and text. The audio features are learned with a convolution neural network (CNN) and a Bi-directional Gated Recurrent Unit (Bi-GRU) network.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about LiQuiD-MIMO Radar: Distributed MIMO Radar with Low-Bit Quantization
- Log in to post comments
Distributed MIMO radar is known to achieve superior sensing performance by employing widely separated antennas. However, it is challenging to implement a low-complexity distributed MIMO radar due to the complex operations at both the receivers and the fusion center. This work proposes a low-bit quantized distributed MIMO (LiQuiDMIMO) radar to significantly reduce the burden of signal acquisition and data transmission. In the LiQuiD-MIMO radar, the widely-separated receivers are restricted to operating with low-resolution ADCs and deliver the low-bit quantized data to the fusion center.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
Reconstructing images using brain signals of imagined visuals may provide an augmented vision to the disabled, leading to the advancement of Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) technology. The recent progress in deep learning has boosted the study area of synthesizing images from brain signals using Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN). In this work, we have proposed a framework for synthesizing the images from the brain activity recorded by an electroencephalogram (EEG) using small-size EEG datasets.
- Categories:
 109 Views
109 Views
The development of semi-supervised learning (SSL) has in recent years largely focused on the development of new consistency regularization or entropy minimization approaches, often resulting in models with complex training strategies to obtain the desired results. In this work, we instead propose a novel approach that explicitly incorporates the underlying clustering assumption in SSL through extending a recently proposed differentiable clustering module. Leveraging annotated data to guide the cluster centroids results in a simple end-to-end trainable deep SSL approach.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views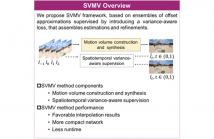
- Read more about SVMV: SPATIOTEMPORAL VARIANCE-SUPERVISED MOTION VOLUME FOR VIDEO FRAME INTERPOLATION
- Log in to post comments
High-performance video frame interpolation is challenging for complex scenes with diverse motion and occlusion characteristics. Existing methods, deploying off-the-shelf flow estimators to acquire initial characterizations refined by multiple subsequent models, often require heavy network architectures that are not practical for resource constrained systems. We investigate the unary potentials of the characterizations to improve efficiency.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views