
IEEE ICASSP 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2023 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
- Read more about Untrained graph neural networks for denoising
- Log in to post comments
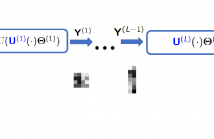
A fundamental problem in signal processing is to denoise a signal. While there are many well-performing methods for denoising signals defined on regular domains, including images defined on a two-dimensional pixel grid, many important classes of signals are defined over irregular domains that can be conveniently represented by a graph. This paper introduces two untrained graph neural network architectures for graph signal denoising, develops theoretical guarantees for their denoising capabilities in a simple setup, and provides empirical evidence in more general scenarios.
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views
- Read more about Feature Selection and Text Embedding For Detecting Dementia from Spontaneous Cantonese
- Log in to post comments
Dementia is a severe cognitive impairment that affects the health of older adults and creates a burden on their families and caretakers. This paper analyzes diverse hand-crafted features extracted from spoken languages and selects the most discriminative ones for dementia detection. Recently, the performance of dementia detection has been significantly improved by utilizing Transformer-based models that automatically capture the structural and linguistic properties of spoken languages. We investigate Transformer-based features and propose an end-to-end system for dementia detection.
ICASSP2023.pdf
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views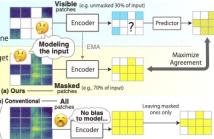
- Read more about MASKED MODELING DUO: LEARNING REPRESENTATIONS BY ENCOURAGING BOTH NETWORKS TO MODEL THE INPUT
- Log in to post comments
Masked Autoencoders is a simple yet powerful self-supervised learning method. However, it learns representations indirectly by reconstructing masked input patches. Several methods learn representations directly by predicting representations of masked patches; however, we think using all patches to encode training signal representations is suboptimal. We propose a new method, Masked Modeling Duo (M2D), that learns representations directly while obtaining training signals using only masked patches.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about Federated Intelligent Terminals Facilitate Stuttering Monitoring
- Log in to post comments
Stuttering is a complicated language disorder. The most common form of stuttering is developmental stuttering, which begins in childhood. Early monitoring and intervention are essential for the treatment of children with stuttering. Automatic speech recognition technology has shown its great potential for non-fluent disorder identification, whereas the previous work has not considered the privacy of users' data. To this end, we propose federated intelligent terminals for automatic monitoring of stuttering speech in different contexts.
- Categories:
 89 Views
89 Views
- Read more about COLUMN-BASED MATRIX APPROXIMATION WITH QUASI-POLYNOMIAL STRUCTURE
- Log in to post comments
A novel matrix completion problem is considered herein: observations based on fully sampled columns and quasi-polynomial side information is exploited. The framework is motivated by quantum chemistry problems wherein full matrix computation is expensive, but partial computations only lead to column information. The proposed algorithm successfully estimates the row-space of a true matrix given a priori knowledge of the true matrix. A theoretical error bound is provided, which captures the possible inaccuracies of the side information.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Recursive/Iterative Unique Projection-Aggregation Decoding of Reed-Muller Codes
- Log in to post comments
We describe recursive unique projection-aggregation (RUPA) decoding and iterative unique projection-aggregation (IUPA) decoding of Reed-Muller (RM) codes, which remove non-unique projections from the recursive projection-aggregation (RPA) and iterative projection-aggregation (IPA) algorithms respectively.
We show that these algorithms have competitive error-correcting performance while requiring up to 95% projections less than the baseline RPA algorithm.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Active selection of source patients in transfer learning for epileptic seizure detection using Riemannian Manifold
- Log in to post comments
Epileptic seizure detection from long recordings of scalp electroencephalography (EEG) is a challenging task owing to their unpredictability in nature with the inclusion of noise, artifacts and subject dependency. We hypothesize that selection of training EEG data plays important role in the model performance. Thus, we introduced an active learning based training data selection and modification method with a Riemannian geometry, centroid alignment, tangent space mapping and a support vector machine classifier.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Restoration of Time-Varying Graph Signals using Deep Algorithm Unrolling
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a restoration method of time-varying graph signals, i.e., signals on a graph whose signal values change over time, using deep algorithm unrolling. Deep algorithm unrolling is a method that learns parameters in an iterative optimization algorithm with deep learning techniques. It is expected to improve convergence speed and accuracy while the iterative steps are still interpretable. In the proposed method, the minimization problem is formulated so that the time-varying graph signal is smooth both in time and spatial domains.
- Categories:
 76 Views
76 Views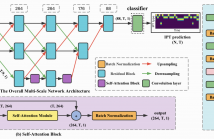
- Read more about Frame-Level Multi-Label Playing Technique Detection Using Multi-Scale Network and Self-Attention Mechanism
- Log in to post comments
Instrument playing technique (IPT) is a key element of musical presentation. However, most of the existing works for IPT detection only concern monophonic music signals, yet little has been done to detect IPTs in polyphonic instrumental solo pieces with overlapping IPTs or mixed IPTs. In this paper, we formulate it as a framelevel multi-label classification problem and apply it to Guzheng, a Chinese plucked string instrument. We create a new dataset, Guzheng Tech99, containing Guzheng recordings and onset, offset, pitch, IPT annotations of each note.
FRAME(1).pdf
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Block-Based Color Constancy: The Deviation of Salient Pixels
- Log in to post comments
We recently proposed a color constancy method based on the observations that the human visual system might be "discounting the illuminant" by using space-average color and the highest luminance patches. Based on these observations, our algorithm relies on two assumptions: (i) there are several bright pixels in the scene, and (ii) the world is gray, on average. The main idea of the algorithm is to estimate the illuminant by finding the deviation of the brightest pixels from the gray value. During experiments, we observed that some pixels decrease the performance of the method.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views