
IEEE ICASSP 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2023 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Delay-aware Backpressure Routing Using Graph Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
We propose a throughput-optimal biased backpressure (BP) algorithm for routing, where the bias is learned through a graph neural network that seeks to minimize end-to-end delay. Classical BP routing provides a simple yet powerful distributed solution for resource allocation in wireless multi-hop networks but has poor delay performance. A low-cost approach to improve this delay performance is to favor shorter paths by incorporating pre-defined biases in the BP computation, such as a bias based on the shortest path (hop) distance to the destination.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views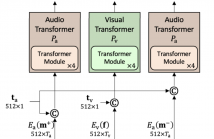
- Read more about ModEFormer: Modality-preserving embedding for audio-video synchronization using transformers
- Log in to post comments
Lack of audio-video synchronization is a common problem during television broadcasts and video conferencing, leading to an unsatisfactory viewing experience. A widely accepted paradigm is to create an error detection mechanism that identifies the cases when audio is leading or lagging. We propose ModEFormer, which independently extracts audio and video embeddings using modality-specific transformers.
- Categories:
 172 Views
172 Views
- Read more about A Statistical Interpretation of the Maximum Subarray Problem
- Log in to post comments
Maximum subarray is a classical problem in computer science that given an array of numbers aims to find a contiguous subarray with the largest sum. We focus on its use for a noisy statistical problem of localizing an interval with a mean different from background. While a naive application of maximum subarray fails at this task, both a penalized and a constrained version can succeed.
Max_Subarray_video.pdf
- Categories:
 73 Views
73 Views
This paper investigates negative sampling for contrastive learning in the context of audio-text retrieval. The strategy for negative sampling refers to selecting negatives (either audio clips or textual descriptions) from a pool of candidates for a positive audio-text pair. We explore sampling strategies via model-estimated within-modality and cross-modality relevance scores for audio and text samples. With a constant training setting on the retrieval system from [1], we study eight sampling strategies, including hard and semi-hard negative sampling.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about IMPROVING MUSIC GENRE CLASSIFICATION FROM MULTI-MODAL PROPERTIES OF MUSIC AND GENRE CORRELATIONS PERSPECTIVE
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views- Read more about Joint Unmixing And Demosaicing Methods For Snapshot Spectral Images
- Log in to post comments
Recent technological advances in design and processing speed have successfully demonstrated a new snapshot mosaic imaging sensor architecture (SSI), allowing miniaturized platforms to efficiently acquire the spatio-spectral content of the dynamic scenes from a single exposure. However, SSI systems have a fundamental trade-off between spatial and spectral resolution because they associate each pixel with a specific spectral band.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about SD-PINN: Physics Informed Neural Networks for Spatially Dependent PDEs
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Modeling the Wave Equation Using Physics-Informed Neural Networks Enhanced with Attention to Loss Weights
- Log in to post comments
Presentation for ICASSP 2023: Modeling the Wave Equation Using Physics-Informed Neural Networks Enhanced with Attention to Loss Weights.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about A NOVEL STATE CONNECTION STRATEGY FOR QUANTUM COMPUTING TO REPRESENT AND COMPRESS DIGITAL IMAGES
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
Quantum image processing draws a lot of attention due to faster data computation and storage compared to classical data processing systems. Converting classical image data into the quantum domain and state label preparation complexity is still a challenging issue. The existing techniques normally connect the pixel values and the state position directly. Recently, the EFRQI (efficient flexible representation of the quantum image) approach uses an auxiliary qubit that connects the pixel-representing qubits to the state position qubits via Toffoli gates to reduce state connection.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about Wireless location tracking via complex-domain Super MDS with time series self-localization information
- Log in to post comments
We propose a wireless localization algorithm based on complex-domain super multidimensional scaling (CD-SMDS) augmented with a self-localization (SL) component, whereby each target tracks its own motion by incorporating bearing in- formation, obtained e.g., from integrated inertial sensors.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views