
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
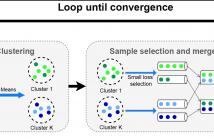
- Read more about Learning with Non-Uniform Label Noise: A Cluster-Dependent Weakly Supervised Approach
- Log in to post comments
Learning with noisy labels is a challenging task in machine learning.
Furthermore in reality, label noise can be highly non-uniform
in feature space, e.g. with higher error rate for more difficult samples.
Some recent works consider instance-dependent label noise
but they require additional information such as some cleanly labeled
data and confidence scores, which are usually unavailable or costly
to obtain. In this paper, we consider learning with non-uniform label
noise that requires no such additional information. Inspired by
poster-3508.pdf
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about Can Large-scale Vocoded Spoofed Data Improve Speech Spoofing Countermeasure with a Self-supervised Front End?
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
A speech spoofing countermeasure (CM) that discriminates between unseen spoofed and bona fide data requires diverse training data. While many datasets use spoofed data generated by speech synthesis systems, it was recently found that data vocoded by neural vocoders were also effective as the spoofed training data. Since many neural vocoders are fast in building and generation, this study used multiple neural vocoders and created more than 9,000 hours of vocoded data on the basis of the VoxCeleb2 corpus.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Enhancing GAN Performance through Neural Architecture Search and Tensor Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have emerged as a powerful tool for generating high-fidelity content. This paper presents a new training procedure that leverages Neural Architecture Search (NAS) to discover the optimal architecture for image generation while employing the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) repulsive loss for adversarial training. Moreover, the generator network is compressed using tensor decomposition to reduce its computational footprint and inference time while preserving its generative performance.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about MOTION TRANSFER-DRIVEN INTRA-CLASS DATA AUGMENTATION FOR FINGER VEIN RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Finger vein recognition (FVR) has emerged as a secure biometric technique because of the confidentiality of vascular bio-information. Recently, deep learning-based FVR has gained increased popularity and achieved promising performance. However, the limited size of public vein datasets has caused overfitting issues and greatly limits the recognition performance.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Multilingual and Fully Non-Autoregressive ASR with Large Language Model Fusion: A Comprehensive Study
- Log in to post comments
In the era of large models, the autoregressive nature of decoding often results in latency serving as a significant bottleneck. We propose a non-autoregressive LM-fused ASR system that effectively leverages the parallelization capabilities of accelerator hardware. Our approach combines the Universal Speech Model (USM) and the PaLM 2 language model in per-segment scoring mode, achieving an average relative WER improvement across all languages of 10.8% on FLEURS and 3.3% on YouTube captioning.
ICASSP2024_slides.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Multicast Transmission Design With Enhanced DOF For Mimo Coded Caching Systems
- Log in to post comments
Integrating coded caching (CC) into multi-input multi-output (MIMO) setups significantly enhances the achievable degrees of freedom (DoF). We consider a cache-aided MIMO configuration with a CC gain t, where a server with L Tx-antennas communicates with K users, each equipped with G Rx-antennas. Similar to existing works, we also extend a core CC approach, designed initially for multi-input single-output (MISO) scenarios, to the MIMO setup.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about SGT: SELF-GUIDED TRANSFORMER FOR FEW-SHOT SEMANTIC SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
For the few-shot segmentation (FSS) task, existing methods
attempt to capture the diversity of new classes by fully uti-
lizing the limited support images, such as cross-attention and
prototype matching. However, they often overlook the fact
that there is variability in different regions of the same ob-
ject, and intra-image similarity is higher than inter-image sim-
ilarity.To address these limitations, a Self-Guided Trans-
former (SGT) is proposed by leveraging intra-image similar-
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about Scaling NVIDIA’s Multi-Speaker Multi-Lingual TTS Systems with Zero-Shot TTS to Indic Languages
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we describe the TTS models developed by NVIDIA for the MMITS-VC (Multi-speaker, Multi-lingual Indic TTS with Voice Cloning) 2024 Challenge. In Tracks 1 and 2, we utilize RAD-MMM to perform few-shot TTS by training additionally on 5 minutes of target speaker data. In Track 3, we utilize P-Flow to perform zero-shot TTS by training on the challenge dataset as well as external datasets. We use HiFi-GAN vocoders for all submissions.
- Categories:
 126 Views
126 Views
- Read more about Learning Graphs and Simplicial Complexes from Data
- Log in to post comments
Graphs are widely used to represent complex information and signal domains with irregular support. Typically, the underlying graph topology is unknown and must be estimated from the available data. Common approaches assume pairwise node interactions and infer the graph topology based on this premise. In contrast, our novel method not only unveils the graph topology but also identifies three-node interactions, referred to in the literature as second-order simplicial complexes (SCs).
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
Music source separation (MSS) aims to separate a music recording into multiple musically distinct stems, such as vocals, bass, drums, and more. Recently, deep learning approaches such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have been used, but the improvement is still limited. In this paper, we propose a novel frequency-domain approach based on a Band-Split RoPE Transformer (called BS-RoFormer).
- Categories:
 63 Views
63 Views