- Transducers
- Spatial and Multichannel Audio
- Source Separation and Signal Enhancement
- Room Acoustics and Acoustic System Modeling
- Network Audio
- Audio for Multimedia
- Audio Processing Systems
- Audio Coding
- Audio Analysis and Synthesis
- Active Noise Control
- Auditory Modeling and Hearing Aids
- Bioacoustics and Medical Acoustics
- Music Signal Processing
- Loudspeaker and Microphone Array Signal Processing
- Echo Cancellation
- Content-Based Audio Processing
- Read more about END-TO-END JOINT LEARNING OF NATURAL LANGUAGE UNDERSTANDING AND DIALOGUE MANAGER
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Joint Modeling of Accents and Acoustics for Multi-Accent Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about INFLUENCE OF THE NUMBER OF LOUDSPEAKERS ON THE TIMBRE IN MIXED-ORDER AMBISONICS REPRODUTION
- Log in to post comments
Ambisonics is a series of flexible spatial sound systems based on spatial harmonics decomposition and each order approximation of sound field. Accuracy and complexity of system increase with order. Considering that the horizontal localization resolution of human hearing is higher than vertical resolution, mixed-order Ambisonics (MOA) reconstructs horizontal sound field with higher order spatial harmonics, while reconstructs vertical sound field with lower order spatial harmonics, and thereby reaches a compromise between the perceptual performance and the complexity of system.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about AN EFFICIENT TARGET LOCALIZATION ESTIMATOR FROM BISTATIC RANGE AND TDOA MEASUREMENTS IN MULTISTATIC RADAR
- Log in to post comments
This paper considers the target localization problem using the hybrid bistatic range and time difference of arrival (TDOA) measurements in multistatic radar. An algebraic closed-form solution to this nonlinear estimation problem is developed through two-stage processing, where the nuisance variables are introduced in the first stage and the localization error of first stage solution is estimated to improve the final target position estimate in the second stage.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views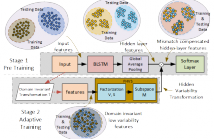
- Read more about FACTORIZED HIDDEN VARIABILITY LEARNING FOR ADAPTATION OF SHORT DURATION LANGUAGE IDENTIFICATION MODELS
- Log in to post comments
Bidirectional long short term memory (BLSTM) recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have recently outperformed other state-of-the-art approaches, such as i-vector and deep neural networks (DNNs) in automatic language identification (LID), particularly when testing with very short utterances (∼3s). Mismatches conditions between training and test data, e.g. speaker, channel, duration and environmental noise, are a major source of performance degradation for LID.
POSTER.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
We propose a novel adversarial multi-task learning scheme, aiming at actively curtailing the inter-talker feature variability while maximizing its senone discriminability so as to enhance the performance of a deep neural network (DNN) based ASR system. We call the scheme speaker-invariant training (SIT). In SIT, a DNN acoustic model and a speaker classifier network are jointly optimized to minimize the senone (tied triphone state) classification loss, and simultaneously mini-maximize the speaker classification loss.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Adversarial Teacher-Student Learning for Unsupervised Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
The teacher-student (T/S) learning has been shown effective in unsupervised domain adaptation ts_adapt. It is a form of transfer learning, not in terms of the transfer of recognition decisions, but the knowledge of posteriori probabilities in the source domain as evaluated by the teacher model. It learns to handle the speaker and environment variability inherent in and restricted to the speech signal in the target domain without proactively addressing the robustness to other likely conditions. Performance degradation may thus ensue.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views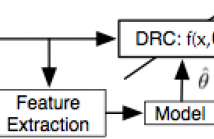
- Read more about FEATURE DESIGN USING AUDIO DECOMPOSITION FOR INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF THE DYNAMIC RANGE COMPRESSOR
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a method of controlling the dynamic range compressor using sound examples. Our earlier work showed the effectiveness of random forest regression to map acoustic features to effect control parameters. We extend this work to address the challenging task of extracting relevant features when audio events overlap. We assess differ- ent audio decomposition approaches such as onset event detection, NMF, and transient/stationary audio separation using ISTA and compare feature extraction strategies for each case.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about FEATURE DESIGN USING AUDIO DECOMPOSITION FOR INTELLIGENT CONTROL OF THE DYNAMIC RANGE COMPRESSOR
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a method of controlling the dynamic range compressor using sound examples. Our earlier work showed the effectiveness of random forest regression to map acoustic features to effect control parameters. We extend this work to address the challenging task of extracting relevant features when audio events overlap. We assess differ- ent audio decomposition approaches such as onset event detection, NMF, and transient/stationary audio separation using ISTA and compare feature extraction strategies for each case.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views