ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2016 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics.
- Read more about ESTIMATION OF TDOA FOR ROOM REFLECTIONS BY ITERATIVE WEIGHTED L1 CONSTRAINT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Theoretical guarantees for Poisson disk sampling using pair correlation function
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we study the problem of generating uniform random
point samples on a domain of d-dimensional space based on a minimum
distance criterion between point samples (Poisson-disk sampling
or PDS). First, we formally define PDS via the pair correlation
function (PCF) to quantitatively evaluate properties of the sampling
process. Surprisingly, none of the existing PDS techniques
satisfy both uniformity and minimum distance criterion, simultaneously.
These approaches typically create an approximate PDS with
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views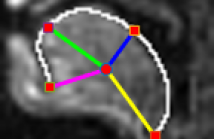
- Read more about EXTRACTION OF TONGUE CONTOUR IN REAL-TIME MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING SEQUENCES
- Log in to post comments
Real-time magnetic resonance imaging (rtMRI) is becoming a practical tool in speech production research and language pathology observation. It is still a challenge to extract the tongue contour accurately in rtMRI sequences, since tongue is a soft tissue and often touches other organs such as lips and upper mandible. This paper proposes a novel semi-automatic tongue contour extraction method from rtMRI sequences. The initial boundary image is obtained by combined multi-directional Sobel operators in tongue movement region; then a boundary intensity map is constructed to find the most probable tongue contour points by searching for the optimal boundary route with Viterbi algorithm; finally the tongue contour is obtained using B-Spline approximation. The proposed method could obtain accurate tongue contour from rtMRI sequences, even in the cases that some parts of tongue touch other organs. Experiments demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about A NEW ARRAY GEOMETRY FOR DOA ESTIMATION WITH ENHANCED DEGREES OF FREEDOM
- Log in to post comments
This work presents a new array geometry, which is capable of providing $O(M^2N^2)$ degrees of freedom (DOF) using only $MN$ physical sensors via utilizing the second-order statistics of the received data. This new array is composed of multiple, identical minimum redundancy subarrays, whose positions follow a minimum redundancy configuration. Thus the new array is a minimum redundancy array (MRA) of MRA subarrays, and is termed {\em nested MRA}. The sensor positions, aperture length, and the number of DOF of the new array can be predicted if these parameters of MRA subarrays are given.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about Imaging in Radio Interferometry by Iterative Subset Scanning Using a Modified AMP Algorithm
- Log in to post comments
Imaging techniques in radio interferometry often face a significant challenge posed by the large number of antenna signals received, from which the image information needs to be extracted. Beamforming is envisaged to reduce the rate required for transporting data from groups of antennas to a central site for further processing. We propose a novel method for image reconstruction based on the iterative scanning of a region of interest, combined with randomized beamforming. A modified approximate message-passing algorithm
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about EQUALIZATION MATCHING OF SPEECH RECORDINGS IN REAL-WORLD ENVIRONMENTS
- Log in to post comments
When different parts of speech content such as voice-overs and narration are recorded in real-world environments with different acoustic properties and background noise, the difference in sound quality between the recordings is typically quite audible and therefore undesirable. We propose an algorithm to equalize multiple such speech recordings so that they sound like they were recorded in the same environment. As the timbral content of the speech and background noise typically differ considerably, a simple equalization matching results in a noticeable mismatch in the output signals.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about BAYESIAN TUNING FOR SUPPORT DETECTION AND SPARSE SIGNAL ESTIMATION VIA ITERATIVE SHRINKAGE-THRESHOLDING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views- Read more about Signal sparsity estimation from compressive noisy projections via γ-sparsified random matrices
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views- Read more about System-Compatible Robustness Improvement for New Generation DECT Decoders by G.722 Soft-Decision Decoding
- Log in to post comments
The ITU-T Recommendation G.722 about subband adaptive differential pulse code modulation (SB-ADPCM) is the mandatory wideband speech codec in the new generation digital enhanced cordless telephony (NG-DECT). Although in ADPCM the difference signal instead of the original signal is quantized and adaptive prediction is employed, redundancy is yet observed within the quantized samples. In this paper we apply a soft-decision speech decoding technique which exploits this redundancy in terms of a priori knowledge and the channel reliability information to NG-DECT.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views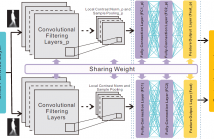
- Read more about Siamese Neural Network based Gait Recognition for Human Identification
- Log in to post comments
As the remarkable characteristics of remote accessed, robust and security, gait recognition has gained significant attention in the biometrics based human identification task. However, the existed methods mainly employ the handcrafted gait features, which cannot well handle the indistinctive inter-class differences and large intra-class variations of human gait in real-world situation. In this paper, we have developed a Siamese neural network based gait recognition framework to automatically extract robust and discriminative gait features for human identification.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views