ICASSP is the world's largest and most comprehensive technical conference on signal processing and its applications. It provides a fantastic networking opportunity for like-minded professionals from around the world. ICASSP 2016 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers and cutting-edge session topics.
- Read more about Mobile Beamforming & Spatially Controlled Relay Communications
- Log in to post comments
We consider stochastic motion planning in single-source single-destination robotic relay networks, under a cooperative beamforming framework. Assuming that the communication medium constitutes a spatiotemporal stochastic field, we propose a
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views- Read more about Audio Word Similarity for Clustering with Zero Resources based on iterative HMM Classification
- Log in to post comments
Recent work on zero resource word discovery makes intensive use of audio fragment clustering to find repeating speech patterns. In the absence of acoustic models, the clustering step traditionally relies on dynamic time warping (DTW) to compare two samples and thus suffers from the known limitations of this technique. We propose a new sample comparison method, called 'similarity by terative classification', that exploits the modeling capacities of hidden Markov models (HMM) with no supervision.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Discriminant Correlation Analysis for Feature Level Fusion with Application to Multimodal Biometrics
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present Discriminant Correlation Analysis (DCA), a feature level fusion technique that incorporates the class associations in correlation analysis of the feature sets. DCA performs an effective feature fusion by maximizing the pair-wise correlations across the two feature sets, and at the same time, eliminating the between-class correlations and restricting the correlations to be within classes.
- Categories:
 121 Views
121 Views- Read more about A Risk-Unbiased Approach to a New Cramer-Rao Bound
- Log in to post comments
How accurately can one estimate a deterministic parameter subject to other unknown deterministic model parameters? The most popular answer to this question is given by the Cramer-Rao bound (CRB). The main assumption behind the derivation of the CRB is local unbiased estimation of all model parameters. The foundations of this work rely on doubting this assumption. Each parameter in its turn is treated as a single parameter of interest, while the other model parameters are treated as nuisance, as their mis-knowledge interferes with the estimation of the parameter of interest.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Dcitionary Learning for Poisson Compressed Sensing
- Log in to post comments
Imaging techniques involve counting of photons striking a detector. Due to fluctuations in the counting process, the measured photon counts are known to be corrupted by Poisson noise. In this paper, we propose a blind dictionary learning framework for the reconstruction of photographic image data from Poisson corrupted measurements acquired by a \emph{compressive} camera.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 ViewsEmbedding the l1 norm in gradient-based adaptive filtering is a popular solution for sparse plant estimation. Supported on the modal analysis of the adaptive algorithm near steady state, this work shows that the optimal sparsity tradeoff depends on filter length, plant sparsity and signal-to-noise ratio. In a practical implementation, these terms are obtained with an unsupervised mechanism tracking the filter weights. Simulation results prove the robustness and superiority of the novel adaptive-tradeoff sparsity-aware method.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views- Read more about Robust Inference for State-Space Models with Skewed Measurement Noise
- Log in to post comments
Filtering and smoothing algorithms for linear discrete-time state-space models with skewed and heavy-tailed measurement noise are presented. The algorithms use a variational Bayes approximation of the posterior distribution of models that have normal prior and skew-t-distributed measurement noise.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views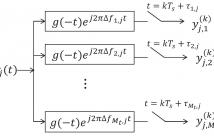
We propose a novel distributed MIMO receiver structure that accounts for multiple carrier frequency offsets (CFOs) and multiple timing offsets (TOs). The proposed structure utilizes a bank of pulse matched filters (one per effective CFO) at each receive antenna, followed by an information symbol detector. Each filter in the bank is sampled at the symbol rate with sampling timing selected according to the corresponding TO. For the proposed receiver configuration, we derive the maximum likelihood (ML) detector for both coded (space-time block code) and uncoded distributed MIMO systems.
IcasspPoster.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views- Read more about COUPLED RANK-(Lm, Ln, ∙) BLOCK TERM DECOMPOSITION BY COUPLED BLOCK SIMULTANEOUS GENERALIZED SCHUR DECOMPOSITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views- Read more about ESTIMATION OF TDOA FOR ROOM REFLECTIONS BY ITERATIVE WEIGHTED L1 CONSTRAINT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views